Editing Your App
Development environment and Editor
The Development environment is designed for application development and testing. When you first create your app, it is automatically deployed to the Development environment.
When working with a ready app, all changes introduced either manually (i.e. in Schema Editor), or with the help of AI Engineer are reflected in the Development environment. Each significant change creates a checkpoint in the version history, which is stored in the Editor tab. Within the Editor, you can safely roll back to any of the previous versions while keeping all the previous iterations.
To access the Editor, switch to the Editor tab or hover over the app preview in the Overview tab. Click the Edit button to be redirected to the Editor tab.
In the Editor tab, you can suggest changes through the chat with the AI Engineer. Any modifications will be reflected in the app preview and recorded in the Version Control sidebar. If you're not satisfied with the result, you can always roll back to a previous version.
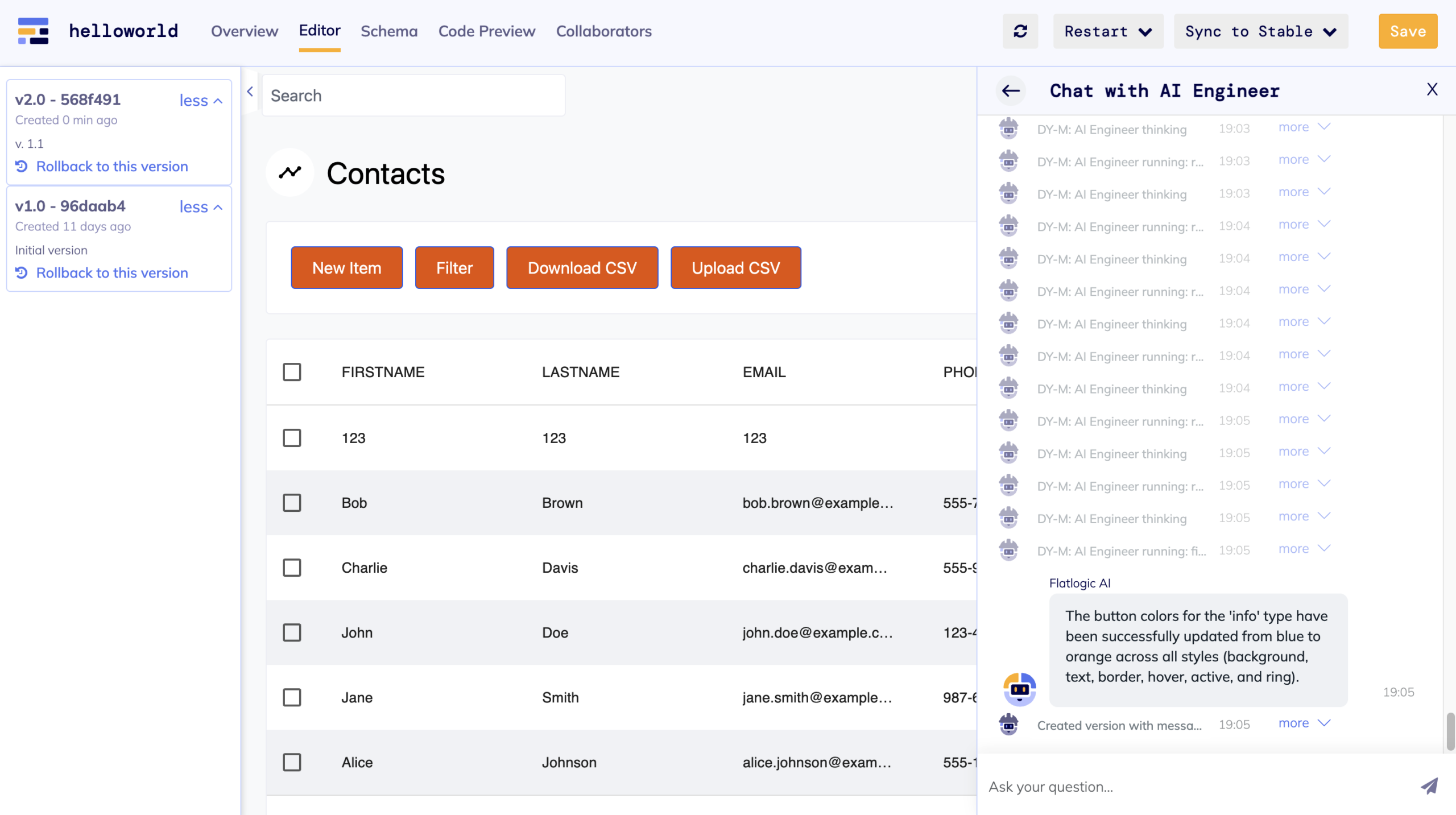
Top bar navigation menu
In the upper-right corner of the Editor tab, you’ll find navigation buttons and actions, which are detailed further in the text below:
Refresh iFrame: Refreshes the iframe on the current page of the app. If you don’t see the changes made by the AI engineer, you can click this button to update.
Restart:
Restart Service: Completes a full restart of the application (restarts front-end and back-end) in the Development environment. Any local changes made will not be saved. Upon restart, the app will pull the latest version from the repository (either from the development environment or from GitHub if a custom repository is connected).
Note: To roll back to the previous version after changes, use “Restart Service” button instead of ‘Save’.
Rebuild Dev Environment: Completely recreates the Dev environment from scratch, creating a new service for front-end and back-end, reinstalling all libraries. A sort of stronger version of “Restart”. If you’ve updated the database schema using the schema editor and pushed the updated code to your GitHub, clicking ‘Rebuild’ will initiate the process of recreating the application, incorporating the latest schema changes from GitHub.
Sync to Stable Environment: All changes made in the Development environment will be synchronized to the Stable environment. In technical terms, the “ai-dev” branch will be merged to the “master” branch and the Stable environment will be rebuilt.
Reset Dev: Resets the Development environment to match the current state of the Stable environment, using the latest version from the stable environment.
Save: Creates a version of the current state in the Development Environment, assigning it a version name that can later be used to rollback changes from or push to the Stable environment.
Few words about Terminology:
Dev Environment: This is your development environment or “sandbox” where you can make any changes you want using AI engineer or the schema editor. When you’re happy with everything, you can move your changes to the Stable environment.
Stable Environment: This is where the final version of your app runs. It’s like the live version that everyone uses.
Repository: This is like a storage space for all the different versions of your project. It keeps everything organized, so you can easily track changes and collaborate with others.
Branch: Imagine a branch as a separate area where you can work on different parts of your project at the same time without mixing them up. It’s a way to keep things organized while you make changes.
Development Branch (ai-dev ): This is where new ideas and features are developed and tested. It’s a safe space to tweak and perfect things before they’re ready for everyone.
Stable Branch (master):This is the main version everyone uses, and it only includes features that have been tested and approved. It’s the reliable version of your app that’s can be ready for public use.
For ready applications, the AI Engineer can help you modify the underlying schema. You can request changes through natural language, such as: "Add an Events entity that displays as a calendar view" or "Create a relationship between Customers and Orders".
The AI Engineer understands these requests and can: add new entities and attributes, modify existing data structures, create relationships between different parts of your application, adjust how data is displayed and interacted with, or delete fields and entities.
Manually editing project Schema
To do that go to the project Schema tab where you can change the project, add and remove entities, and rebuild the project. Here is a video example how to modify schema of your app.
The basic essence of the Schema Editor is that it consists of tables and columns and your work will consist of working with them.
When working with tables you have 2 options - add a new table or delete it (any except the default Users table). Now let's take a look at each of these steps separately.
When working with columns, you have 3 options - add or remove a column, or change the properties of the column.
Working with tables
- Adding the table: to add a table you need to press the '+ Add Table' button (see screenshot below). After clicking the button, a new table will be added and you will be prompted to select a name for this table. Please follow SQL table naming standards. Please choose the name in lower case for better code generation. You can add an unlimited number of tables to the paid plan and the free plan. For example, users, categories, tags, tags1, tags2, etc.
- Deleting the table: deleting a table is very simple - you just need to select the table you want to delete and click the 'Delete Table' button. The table and all columns referring to it will be deleted immediately. Please note that the ‘Users’ table can not be deleted.
Working with columns
- Adding a Column. To create a new column, start by selecting the table where the column will be added. Next, click the
+ Add Columnbutton. This action will open the Edit Column window on the right side of the screen, allowing you to configure the following parameters.:
Note: Our generator adds the column ID itself and makes the connection if necessary: you don't need to add the column ID yourself.
| Name | SQL column name and code property. Use snake or camel case. Note, the column name cannot start with a number. | Name, Title, Name1 |
| Title | Property visible name in user interface | Role, Avatar |
| Type | Column type | string, integer |
The following types are offered to choose from:
| Name | Decription | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| String | stores text data | Hello World! |
| Boolean | stores true/false | true |
| Date time | stores full date only with time | 2022-02-22M09:45:27 |
| Date | stores full date only, without time | 2022-02-22M |
| Decimal | stores fraction | 22.75 |
| Integer | stores integers | 45 |
| Enumeration | stores any value from specified list | 1, 2, 3 |
| Images | stores image files | link |
| Files | stores any raw files | link |
| Relation (one) | one-sided relation capable of storing one of other entity | Employee: [{ name: 'John'}] |
| Relation (many) | two-sided relation capable of storing any number of other entity | Employee: [{ name: 'John' }, { name: 'Joe' }]; |
- Editing a Column. To edit an existing column, simply click on it. The Edit Column menu will appear on the right side of the modal window, displaying the properties available for modification. You can update the following properties: Name, Title, Show in Form, Show in Table. When naming columns, please use camelCase, numbers, and underscores (
_) for consistency and clarity.
Note: The column name cannot start with a number. Also, there cannot be the same-named columns in one table.
- Deleting a column: Deleting a column is done by selecting the column you want to delete and pressing the Delete button. The column should be deleted immediately. You cannot delete the last column in the table.
Saving changes to Development environment
After you made your changes to the schema at the Schema Editor tab, you need to save your changes on your Development environemtnt by clicking on Save button.
Next, the Flatlogic Platform creates a new version at your Development environment for you.
Note that depending on your template type (free community template or paid template), pushing to GitHub may require credits. For paid templates, you'll need to activate the "Push to GitHub" feature for your project, which is a one-time credit cost that unlocks source code access.
Deployment
Next, go back to your Overview tab and click on “Deploy”. This will regenerate your application. More details about deployment you can check by this page: Deploying Your App
If you face any difficulties, please message us on our Discord, Forum, Twitter, or Facebook. We will respond to your inquiry as quickly as possible!