What makes React Native the Future?
A clear advantage of using React Native is it can help you build a native application without having to understand things like Objective-C, JavaScript, Kotlin or Swift. Apps can be developed for platforms such as iOS, Windows Phone, Virtual Reality headsets and helmets, and Android. React Native is a project of Facebook. Technology biggies like Tesla, Airbnb, Samsung, and Wix, along with others are dedicated to creating React Native and the IT-community surrounding it. Google Trends says React Native’s framework popularity has grown during the previous three years. That is very remarkable and it’s not expected to end.
If you want to comprehend the technological underpinnings of utilizing React Native in the mobile environment, it’s necessary to understand all about the framework of React JS. React performs highly because it utilizes Virtual DOM. Firstly, we must remember a Document Object Model (DOM) is the standard cross-platform needed to access documents. Via DOM, you are able to interact with web browsers. However, the foremost issue with DOM is a dynamic and responsive user interface can’t be created.
A virtual DOM is a duplicate of an real DOM. Changes are made only in a specific are of the duplicate. A virtual DOM represents a perfect UI that is able to be reconciled with a real DOM.
In place of utilizing the DOM of a web browser, React Native renders either Android or iOS components.
Consequently the chief trick React Native invokes is the native rendering APIs. The React Native applications create API requests that call native components via JavaScript. Or an Objective-C. React Native utilizes typical UI blocks, just like iOS or Android applications, however there isn’t a WebView or UIWebView.
Any created mobile application ought to be native And if an application is dependent on HTML or JS or CSS, it’s a better choice to improve the mobile form of a web application.
An advantage of using React Native is the option to utilize Expo. That toolchain comes with a lot more APIs besides the ones from React Native. And, it is possible to watch the development progression or you can also test a few of the new aspects of it via Expo’s application. If your project is large or complicated, you will require full play. In regard to a wide-ranging project, it’s a better idea to prepare a mobile application via React Native.
One of the big pluses of utilizing React Native is if the user has experience in website development already, and then it’s simple to learn how to use React Native. Plus tools like Yarn, NPM, ES6 or ES7, and CSS can be used. 
React Native come with a smart system to monitor errors that comprise the ability to track errors, and to show a message or an attempt to recover. That system is extremely efficient for taking care of exceptions that weren’t caught previously.
A huge advantage in using React Native is its community support. By using StackOverflow you can see more than 53K questions related to React Native. Plus, GitHub displays steady growth of the open-source projects that utilize RN.
React Native has hardly any competition in the marketplace. Two, however, are Flutter along with Ionic. We shall now do a comparison between React Native and those competitors.
React Native Versus Flutter
Flutter comes from Google. It’s their attempt to develop a cross-platform kind of mobile framework that lets a developer design a mobile app which works for iOs and Android via Dart language.
Actually, Flutter isn’t that great, according to users, especially in regard to developing an iOS app. To understand, we must first check out the way React Native works.
Both the Android as well as the iOS mobile platforms delivers APIs which communicate with the native environment. This may involve APIs that render native elements or to utilize native iOS technology (i.e. GPS or Bluetooth, etc.). And essentially, React Native gives users a bridge which lets the JS code call native functions via the specific platform.
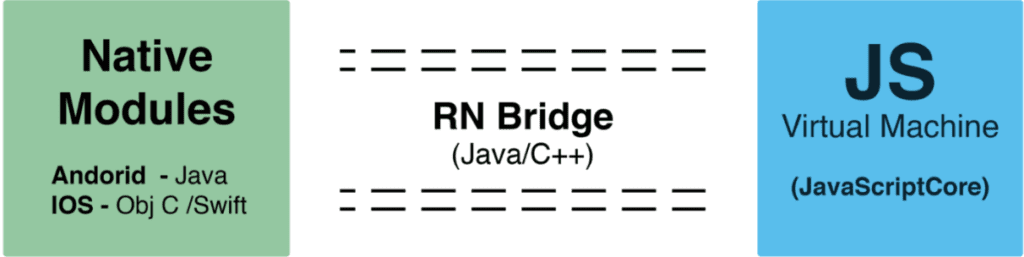
Whenever you create a button via the calling of some abstract purpose like createButton (it is done via the React DOM in the background), React Native transfers that instruction over a bridge that goes to the native platform, then calls Android’s JavaScript function to create a button and the iOS Objective-C function creates a native button for iOS. That principle lets React Native applications appear as and act exactly like a native application.
Go back to Flutter for a moment. It acts more similar to a game engine. Then we see Flutter’s first con. Whenever a createButton function in the Dart code is called, Flutter’s engine is accountable to draw it. Plus within the average library, Flutter attempts to copy the native button’s behavior. It is implemented very well with an Android app, however with an iOS app, it appears far from being native. Firstly, it provides the users with a bad experience, and next, whenever there is a release of a brand-new UI element or some APIs, you must wait until Google updates implementing the native adapter prior to its use.
React Native Versus Ionic
The top con when using an Ionic application is it’s very slow and doesn’t look native whatsoever. That’s because Ionic is merely a Webview wrap that goes overtop the web mechanisms written via CSS and JS, and that causes the application to be dependent on WebView which is very slow. Likewise, it causes you to be accountable to make your application appear and act like a native one, and that’s very complicated.
React Native’s Future
React Native is about to get some changes! It has a few issues of course, and while lots of businesses and crews are using RN development, those issues have become lots more noticeable and there’s a lot more stress in trying to get them resolved. The Facebook crew is upgrading React Native so it can resolve a lot of the issues with the framework.
The top method of understanding this brand-new construction is checking out this great outline from a top RN contributor here.
Comments