
Starting Web App in 2025 Research Results
Introduction
Our annual research on how web applications are started has attracted growing interest and recognition for four consecutive years. Building on the foundation laid in 2022, 2023, and 2024, we continue our efforts to capture the latest trends, tools, and methodologies shaping how web apps are developed.
In 2025, our focus expands to include emerging concepts such as “vibe-coding” and the increasing use of AI web generators. We’ve refined the survey by removing outdated topics and adding new questions to better reflect the rapid evolution of the web development landscape. As in previous years, we aim to understand how web apps are started across the full spectrum of tools, from traditional coding environments to low-code/no-code platforms and AI-assisted solutions.
This year, we also continued collecting data about respondents' roles, engineers, decision-makers, and others, allowing us to examine how professional responsibilities influence development approaches and tool choices.
The 2025 edition of the survey was conducted between April and July. A total of 303 participants from 33 countries took part. Below is a detailed overview of the technologies, frameworks, platforms, and workflows users use to build web applications today.
The results of the previous year's research:
2022 – https://flatlogic.com/starting-web-app-in-2022-research
2023 – https://flatlogic.com/starting-web-app-in-2023-research
2024 – https://flatlogic.com/starting-web-app-in-2024-research
Key outcomes
The key findings of the study, grouped by category, are presented in this section:
Building web applications
-
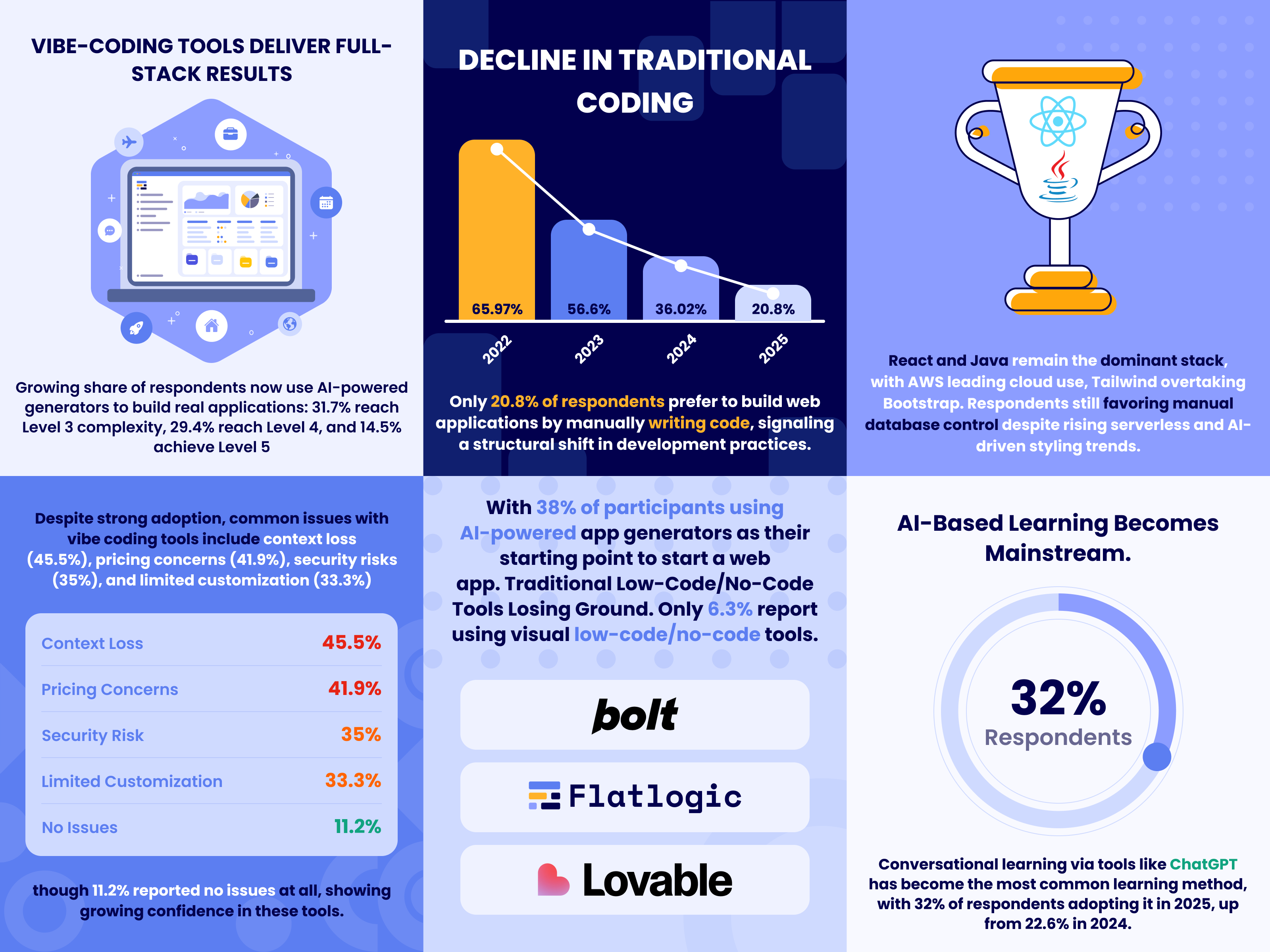
Decline in Traditional Coding: Only 20.8% of respondents prefer to build web applications by manually writing code. This continues a significant downward trend from 36.0% in 2024 and 65.9% in 2022, signaling a structural shift in development practices. Though around 40–50% of professional software engineers still prefer manual coding
-
Tools such as Bolt.new, Flatlogic, and Lovable have gained prominence, with 38% ofparticipants using AI-powered app generators as their starting point to start a web app.
-
Hybrid Approaches on the Rise. 29.7% of respondents now prefer a combined approach, merging manual coding with AI-assisted or low-code solutions to start a web app.
-
Traditional Low-Code/No-Code Tools Losing Ground. Only 6.3% report using visual low-code/no-code tools. This is a significant decline compared to 2024, when WordPress alone accounted for 29.3% of usage.
Vibe-coding tools
- From Experimental to Essential. Vibe-coding has moved from experimental to essential, powerful enough for real applications, yet still maturing in areas like cost transparency and architecture control.
- AI-Generated Codebases Lead. AI-generated codebases are now the most common starting point for web apps, chosen by 38% of respondents, surpassing both free and paid templates.
- Full-Stack Results Achieved. 31.7% of respondents reach Level 3 complexity (frontend apps with backend integration), 29.4% reach Level 4 (custom full-stack apps with CRUD and data), and 14.5% achieve Level 5, production-grade SaaS with advanced features. All numbers self-reported.
- Common Issues. Context loss (45.5%), pricing concerns (41.9%), security risks (35%), and limited customization (33.3%) remain frequent challenges, though 11.2% reported no issues at all.
Technology
- React’s Dominance Continues. With 43.75% adoption, React remains the leading frontend framework. Vue (6.6%) and Angular (5.6%) remain niche.
- Backend Usage Trends. Java is the leading backend usage at 33.7%, followed by serverless platforms and backend-as-a-service (Firebase, Supabase, etc.) at a combined 33%.
- Python and PHP Still Relevant. Python (16.5%) and PHP (10.6%) maintain strong presence, especially in mature or enterprise environments.
- Cloud Platform Preferences. AWS leads (22.4%), followed by Google Cloud (17.5%), Vercel (12.9%), and Cloudflare (6.6%).
- Database Management Stability. 49.8% of respondents still manage databases manually despite headless/serverless options.
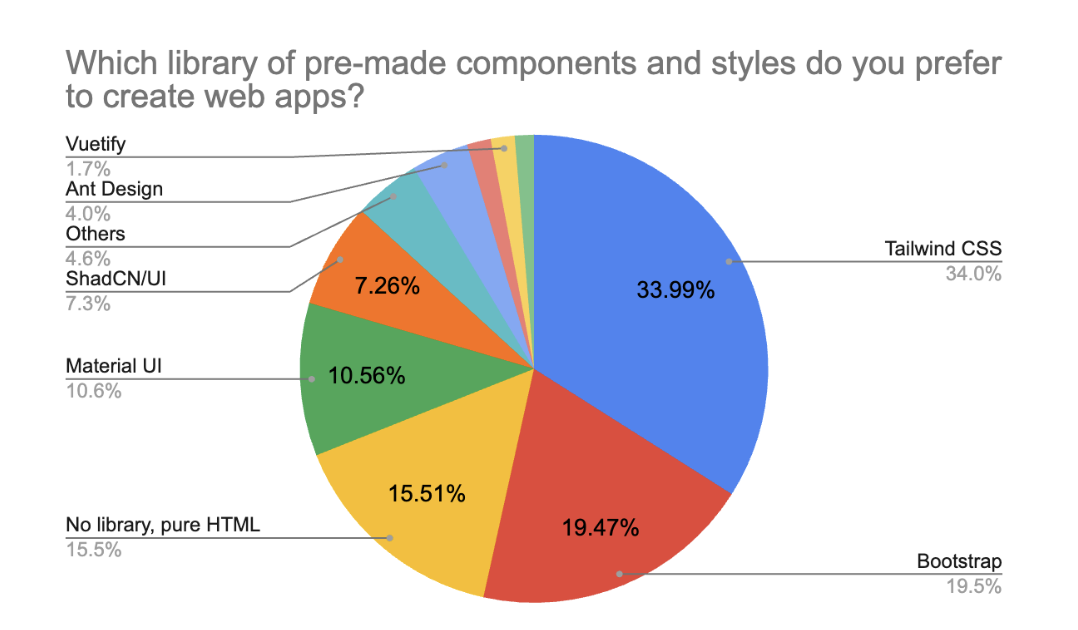
- Styling Trends. Tailwind CSS leads at 34%, surpassing Bootstrap (19.5%). “No styling library” approaches have grown to 15.5%.
Learning to code
- AI-Based Learning Becomes Mainstream. Conversational learning via tools like ChatGPT is the most common method, with 32% adoption in 2025, up from 22.6% in 2024.
- Decline in Online Courses and Video Learning. Online course usage fell from 59.7% in 2023 to 18.1%, and video-based learning dropped from 52.8% to 10.9%.
- Classical Learning Models Nearly Abandoned. Reading programming books (2.3%) and formal university education (3.4%) are least favored. Coding bootcamps dropped to 11.9%.
- Audience Differences. Technical professionals (engineers, students) continue using forums/tutorials, while non-technical users prefer AI-based, conversational formats.
Methodology
The survey included 21 anonymous questions about web development and was completed by 303 participants from 33 countries. With a confidence level of 95% and a margin of error of 5.63%, the survey was conducted from April to July 2025. We intentionally did not define a specific type of web application to gather a broad spectrum of responses and better understand what “web application” means to different people. Participants were primarily recruited through Flatlogic’s digital channels, including onsite messages, blog articles, email campaigns, banner ads, and social media posts. Additionally, paid advertising helped reach engineers from the broader web development community.
All questions in the survey were mandatory, though some allowed open-ended answers to give respondents the freedom to express their views.
If you're interested in reviewing the original questionnaire, you can do so via the provided link. Please note that the form is now outdated and is no longer intended for submission.
Respondent profile
Here is what we know about the participants' profiles.
Experience
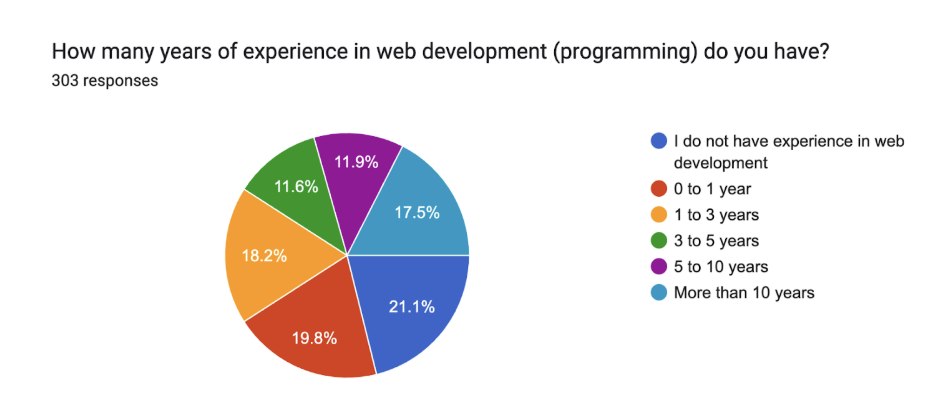
The survey indicates that most participants had at least one year of experience in software development, with a significant portion reporting over 10 years of professional experience in the field.
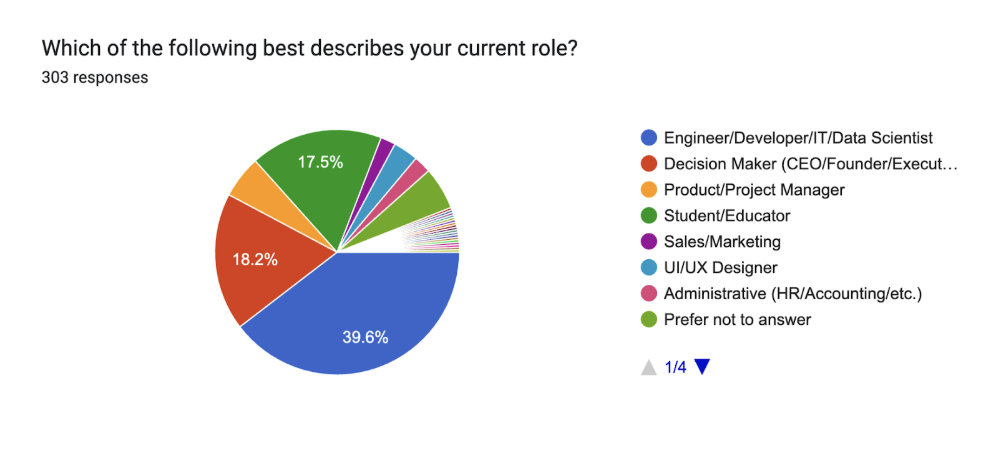
To better understand how web app development practices vary by background, we asked respondents about their professional roles. The majority identified as engineers or developers (39%), followed by decision-makers such as executives and founders (20%), and students (13%). The remaining responses included product managers, project managers, and other roles across business and technical functions. This distribution provides useful context for interpreting preferences in development tools and workflows.
Geography
In total, respondents from 33 countries participated in the study.
Starting web application
How respondents build web applications
In 2025, AI-powered development tools will have overtaken traditional and low-code approaches as the most common way to build web applications. This year, 38% of respondents reported using AI-driven app generators (e.g., Flatlogic, Bolt, Lovable) as their primary method, surpassing all other approaches.
To better reflect this growing category, we added a dedicated response option for AI-powered app generators in this year’s survey. In previous years, respondents who used these tools were grouped under low-code/no-code or hybrid methods, which no longer captured the nuance of how these platforms are used today. As AI tools now offer full-stack scaffolding, real-time modification, and deployable codebases, they have become a distinct workflow and deserve a distinct category.
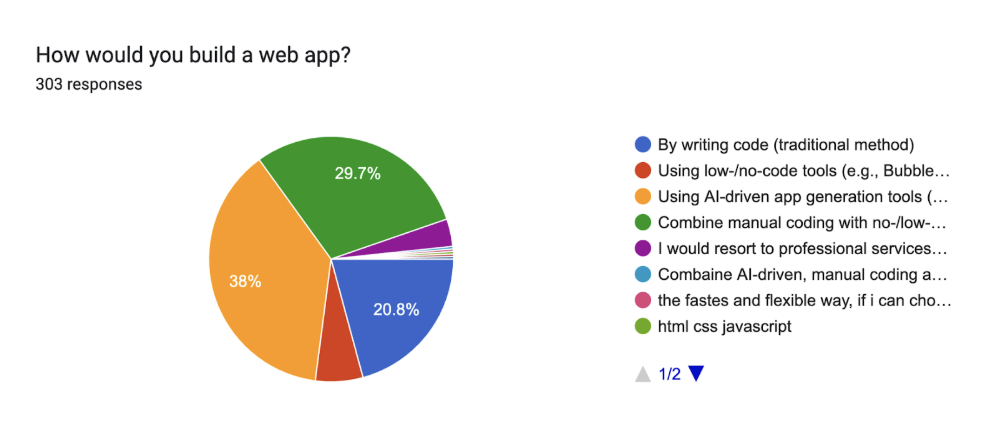
Manual coding continues to decline, just 20.8% of respondents rely on it exclusively, down from 36.0% in 2024. This confirms a multi-year shift away from manual development toward tools that accelerate and assist the early stages of software creation.
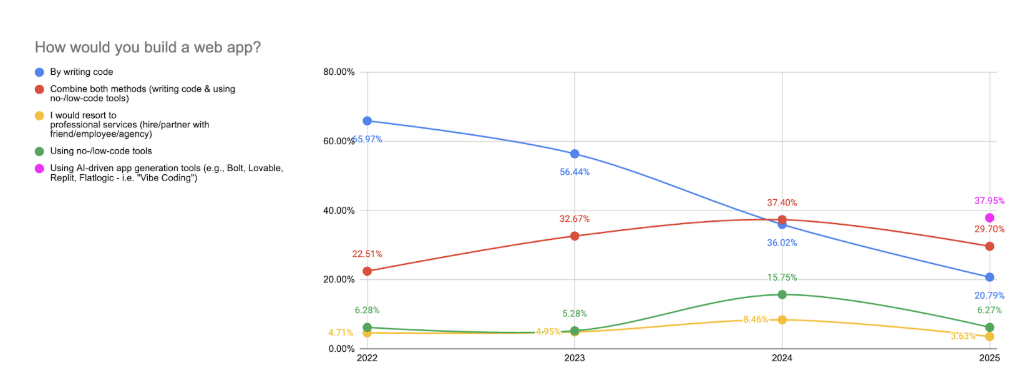
29.7% of respondents said they combine classical coding with low-code/no-code or AI tools. This hybrid approach remains stable and reflects a maturing preference for workflows that balance speed with flexibility and control. Classical low-code/no-code tools (such as Webflow or Bubble) account for just 6.3% of responses. Only 3.6% said they rely on professional development services, a figure that has remained relatively unchanged over time.
These numbers highlight that AI tools are now the center of gravity in early-stage web development. Hybrid approaches continue to grow, while traditional coding is no longer the default starting point for most respondents.
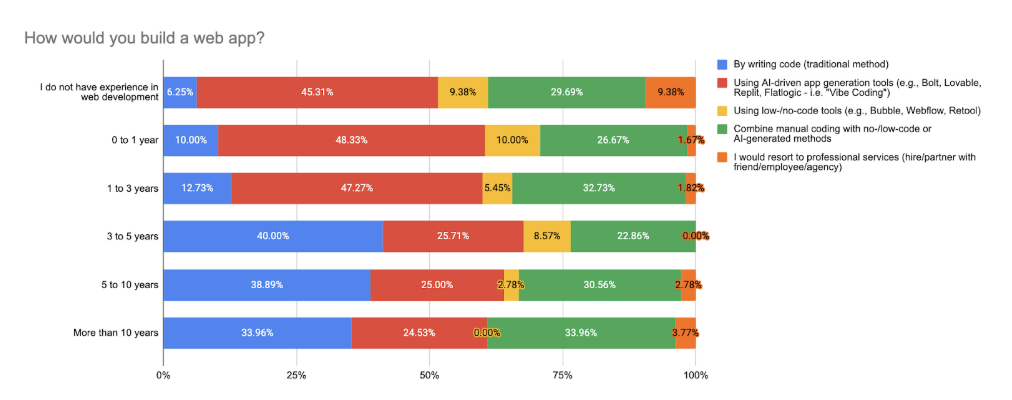
Respondents with less than one year of experience overwhelmingly favor AI-powered tools (48.3%) and hybrid setups (26.7%). They rarely write code from scratch, and only 10% use traditional methods. Similarly, respondents without any prior experience in web development rely on AI tools (45.3%) or low-code platforms, with just 6.2% choosing to code manually.
Those with 1 to 3 years of experience represent a transitional group: 47.3% use AI generators, but a significant 32.7% embrace hybrid workflows. Manual coding remains low (12.7%), reflecting their need for speed while continuing to build core technical skills.
Among respondents with 3 to 10 years of experience, the pattern changes: 40% of those with 3–5 years and 38.9% of those with 5–10 years still prefer to write code manually. AI usage drops to 25–26%, and hybrid strategies become more prominent (22–31%). These respondents often strike a balance between automation and control, using AI where it adds value without fully giving up hands-on development.
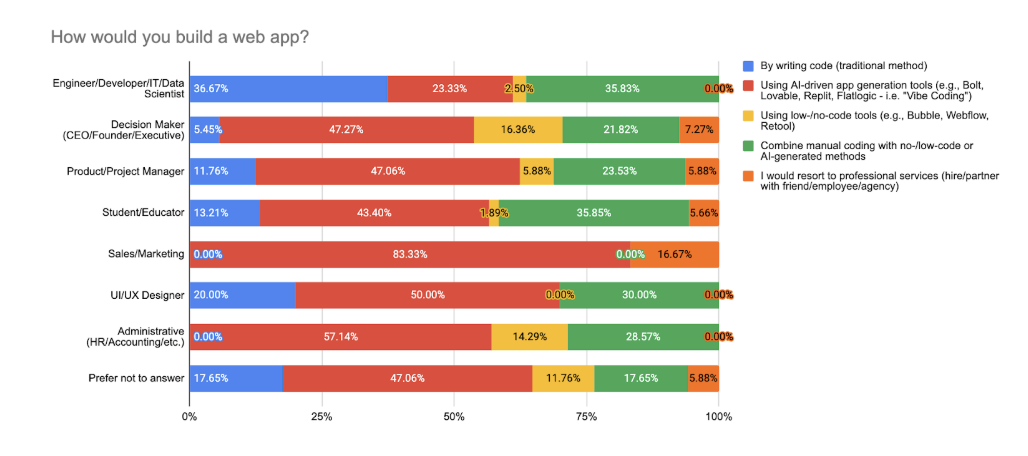
Engineers and developers remain the most divided: around 40–50% still prefer manual coding, but 30% have adopted hybrid methods, and another 20–30% use AI-driven generators. This variety reflects different levels of specialization and team contexts.
Students closely mirror engineers but skew slightly more toward AI adoption, with over 43% using AI generators or hybrid approaches. For them, learning efficiency and rapid prototyping seems to take precedence over deep architectural control.
On the other hand, decision-makers and non-technical roles overwhelmingly rely on AI-based tools (over 70%).
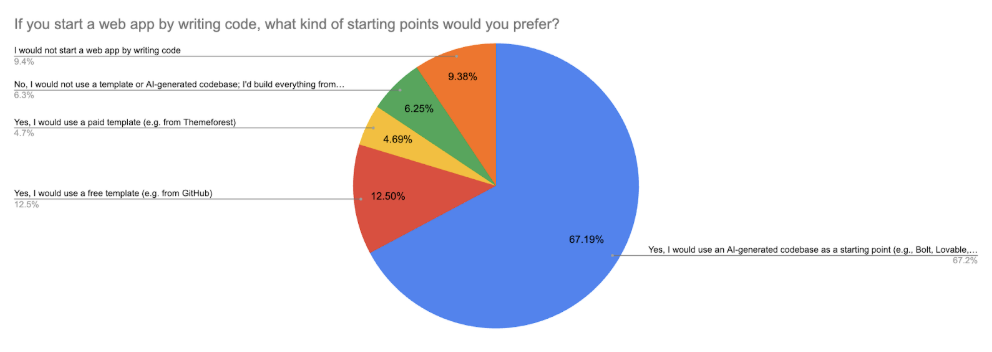
The rise of AI is also evident in how respondents choose to start projects. Among those who build apps with code, 67% said they begin with an AI-generated codebase. This approach is now more common than free templates from GitHub (12.5%) or paid templates (4.7%). Only 9% still choose to build everything from scratch.
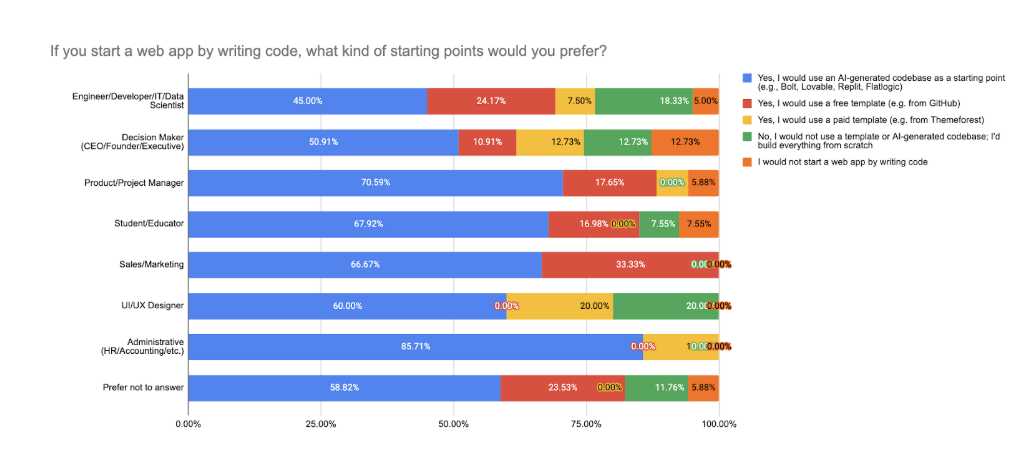
The 2025 data reveals a clear and accelerating shift in how different professional roles approach starting web development projects: AI-generated codebases have become the default across nearly all non-technical groups, while experienced technical users continue to favor hands-on control.
Across executives, creatives, and administrative professionals, AI is not just a supplement, it is the starting point. These roles overwhelmingly rely on AI tools to scaffold applications quickly and without the need for manual setup or technical configuration. Templates, both free and paid, are used sporadically, but they no longer define the workflow.
In contrast, respondents with engineering backgrounds, especially those who span multiple technical domains, remain cautious. They show a strong preference for building from scratch, maintaining control over structure and implementation. For them, AI may support the process, but it does not initiate it.
This divergence reflects a broader pattern: AI is democratizing access to software development, enabling non-technical users to launch applications independently, while more technical users adopt AI more selectively, often to augment, not replace, their workflow.
AI Integrations To Web App Development
This year’s study expanded its focus on artificial intelligence, adding new questions around AI-assisted coding, AI web application generators, and integration complexity. The findings confirm what many in the industry already suspect: AI is no longer experimental but embedded in respondents' daily workflows across experience levels.
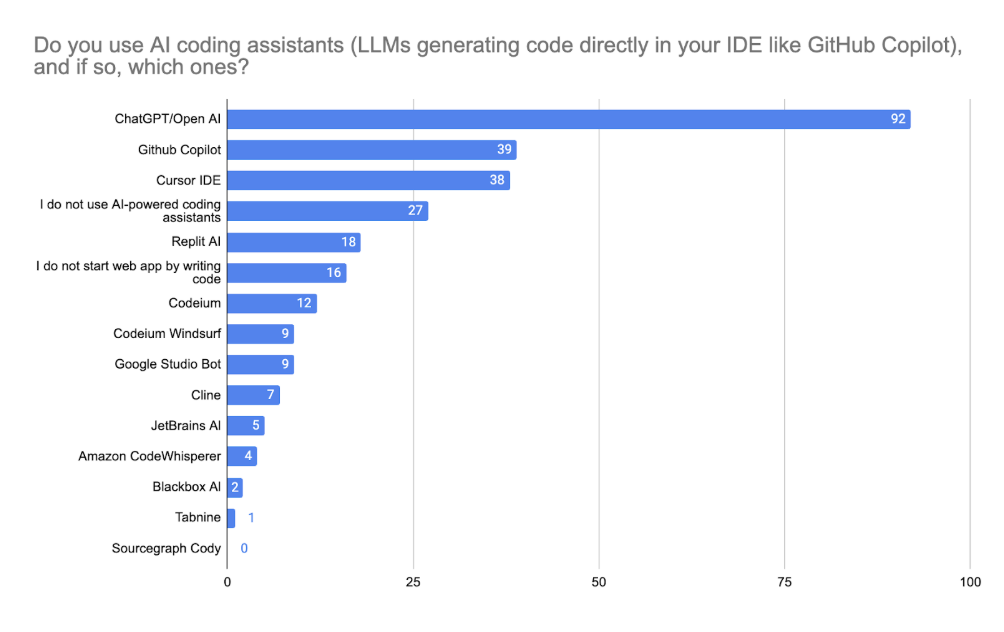
When asked about AI coding assistants integrated directly into their IDEs (such as GitHub Copilot, Cursor, or ChatGPT), the majority of respondents reported regular usage. ChatGPT/OpenAI was the most popular tool (30%), followed by Cursor IDE (12.5%) and GitHub Copilot (12.2%). Only 8.9% of respondents indicated they do not use any AI coding assistant at all, suggesting near-universal adoption among active respondents.
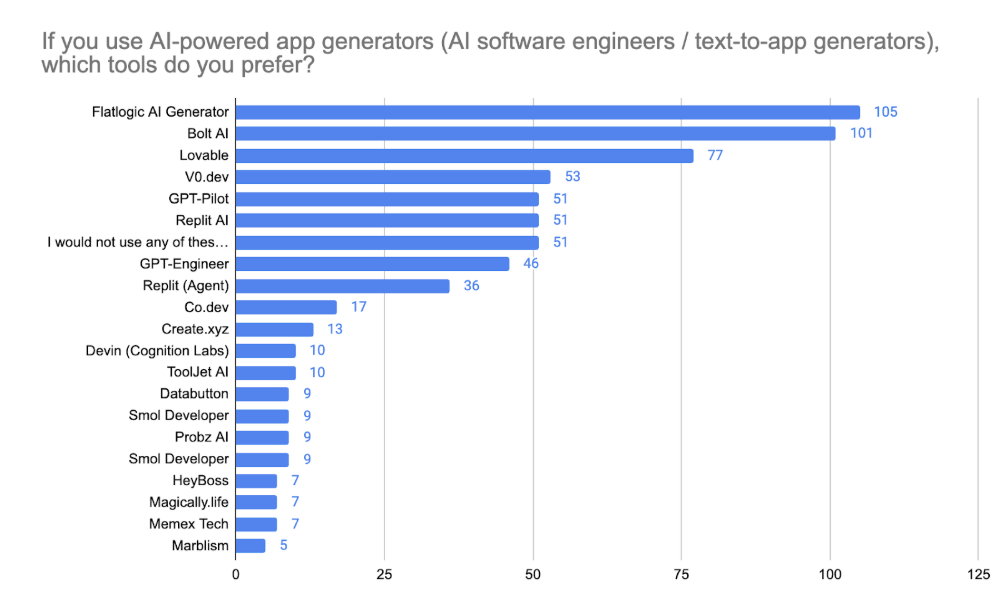
AI-powered app generators, also referred to as AI software engineers or text-to-app tools, are becoming widespread. Tools like Bolt, GPT-Pilot, and Lovable were the most frequently mentioned. However, 15.5% of respondents still said they do not use any of these platforms, reflecting some ongoing skepticism or unmet needs in this emerging category.
Vibe-coding tools
This year, we introduced a dedicated question about vibe-coding tools, a category referring to AI-powered app generators like Flatlogic, Bolt, and Lovable. The decision to include this question stemmed from the growing buzz around vibe-coding in the community. While heavily promoted as a faster, smarter way to build web apps, it was unclear what these tools deliver in practice. Are they just scaffolding tools, or can they truly build production-grade apps? To explore this, we created a five-level framework to measure the real-world complexity of applications built with AI generators:
- Level 1: Static websites (HTML/CSS only, minimal or no JavaScript)
- Level 2: Interactive front-end apps (e.g., React, Vue) with no backend
- Level 3: Front-end apps integrated with external backend services (Firebase, Supabase, REST APIs)
- Level 4: Full-stack apps with custom backend, CRUD logic, authentication, and database integration
- Level 5: Production-grade SaaS or enterprise applications, including roles, permissions, multi-tenancy, payments, and deployment
By segmenting responses across these levels, we gained a clearer picture of what vibe-coding tools achieve and how their output varies by role, use case, and technical depth.
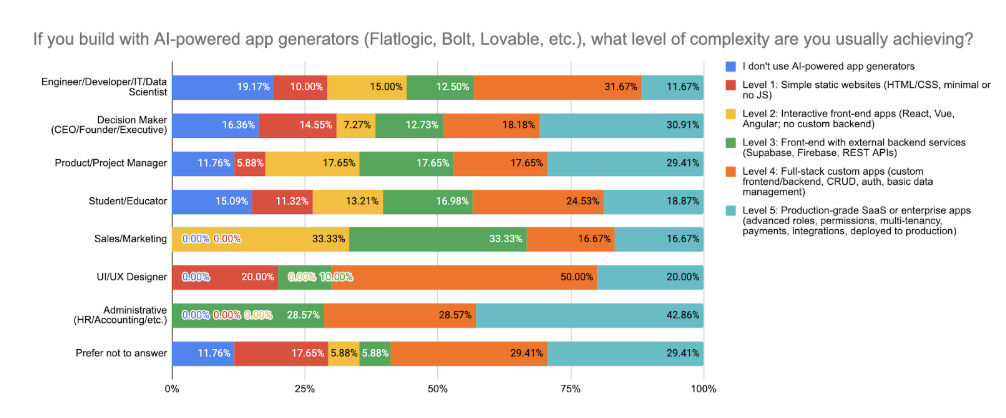
AI-powered app generators are now used to build complex, full-stack applications by a wide range of users. Level 4 complexity, custom apps with backend, CRUD, and data management, is achieved by nearly a third of product managers, students, and admin roles. Level 3, apps integrated with backend services, is common among engineers (31.7%) and decision-makers (30.9%).
Advanced production-level builds (Level 5) are no longer rare, especially among UI/UX designers (20%) and administrative users (42.9%). Only a small portion of respondents, mainly engineers (19.2%) and students (15%), say they don’t use AI app generators at all.
A large number of users reported being able to generate full-stack applications or apps with both front-end and external backend integration. This suggests that modern AI tools are evolving beyond simple UI scaffolds and into territory previously reserved for manual development.
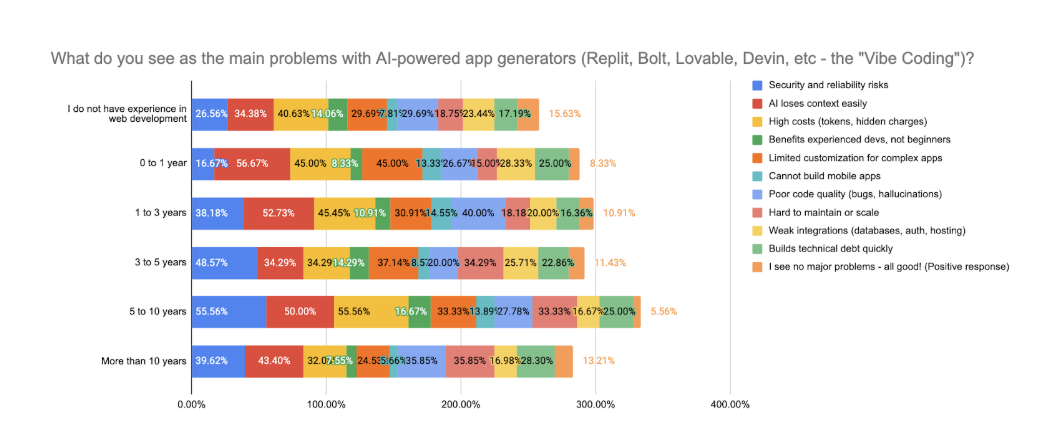
However, respondents also identified several limitations of current AI-driven development platforms:
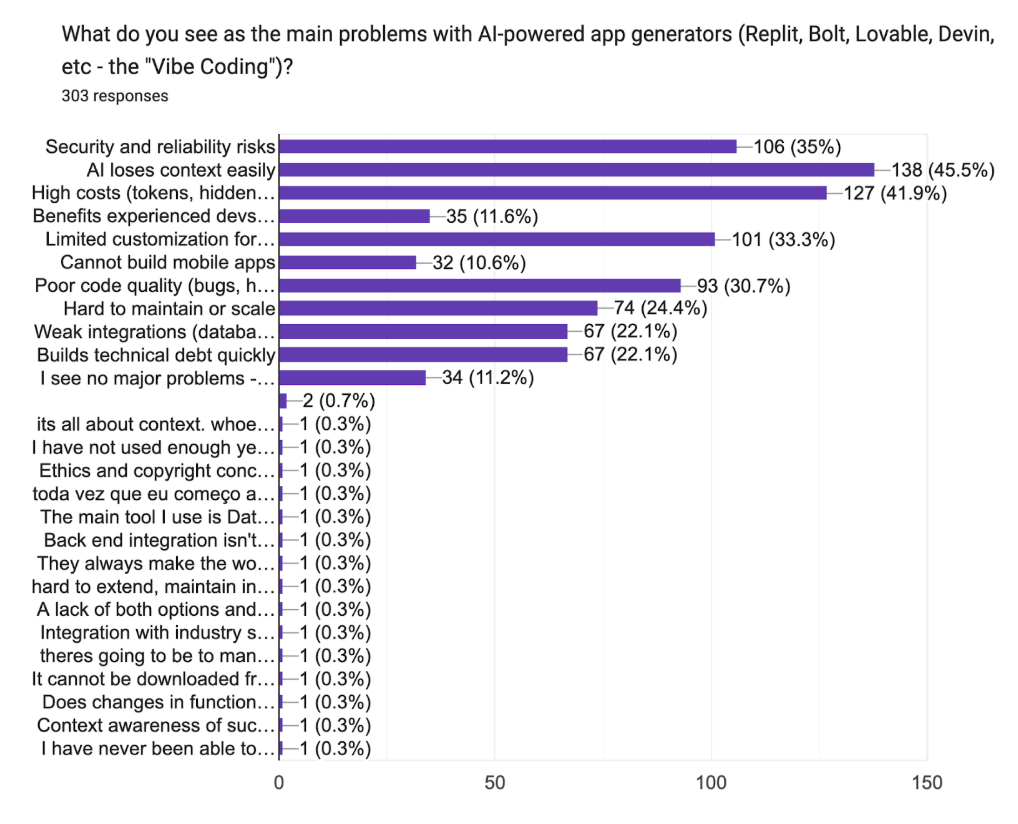
The top concern was AI losing architectural context (45.5%), followed by high or hidden costs (41.9%), and security and reliability risks (35.0%). Limited customization for complex or enterprise-grade apps was cited by 33.3% of respondents, and 30.7% mentioned poor code quality. Interestingly, 11.2% of respondents reported no major issues, highlighting a growing subset of users who consider current AI tools mature enough for production use.
Taken together, the data signals a maturing phase for AI in software development. While some friction remains, especially around customization, pricing, and reliability, AI is now widely used, deeply integrated, and increasingly trusted to handle real development work.
Low-code/no-code tools
In 2025, Low-Code/No-Code tools continue to gain ground, though resistance remains, 28.7% of respondents still said they would not use LCNC tools at all. However, this marks the lowest rejection rate since tracking began in 2022, down from 45% in 2022, 44% in 2023, and 32% in 2024. The data confirms a steady and measurable upward trend in adoption across the board, especially among newer developers and non-technical users.
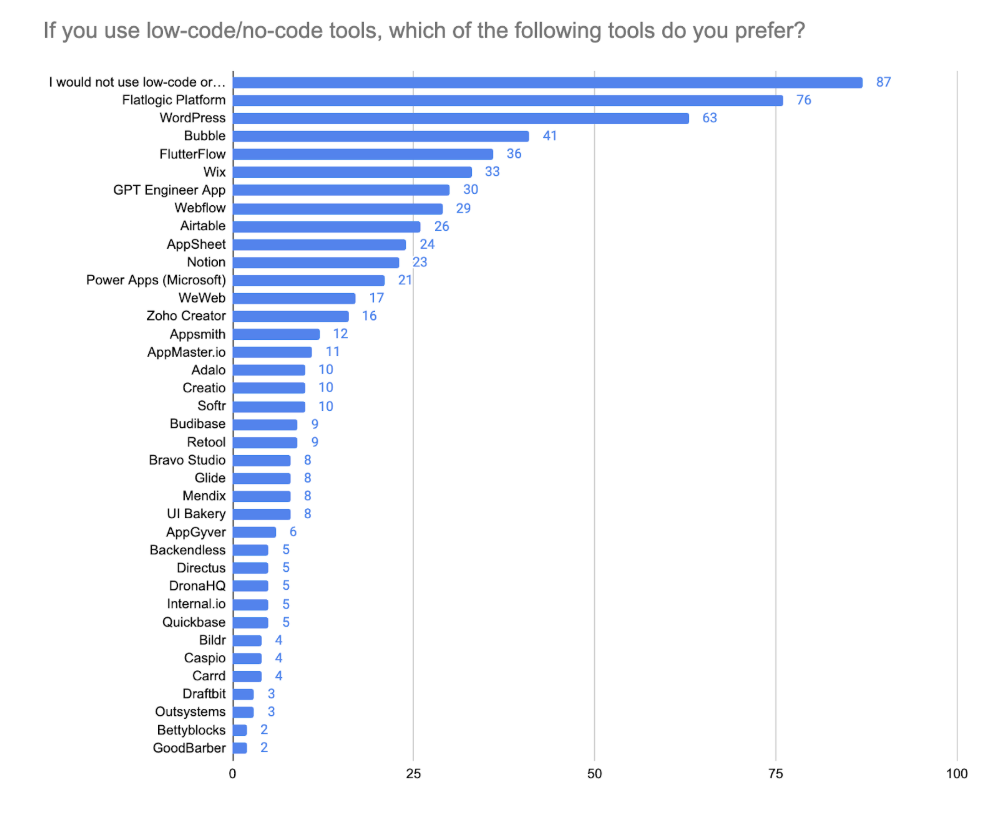
Among those who do adopt LCNC tools, the landscape remains fragmented, but for the first time, we begin to see signs of early consolidation around a few leading platforms. Flatlogic bias was present in the data due to the data collection mechanism.
- Flatlogic Platform was the most frequently mentioned tool in 2025. This suggests growing recognition of Flatlogic’s hybrid approach, combining structured customization and AI-powered scaffolding.
- WordPress maintained strong relevance, continuing its multi-year run as a default tool for web-based content applications and basic CRUD interfaces.
- Bubble is confirming its status as a go-to no-code platform for SaaS builders and internal tooling.
- FlutterFlow is showing increasing momentum, particularly among mobile-focused teams and those seeking unified front-end frameworks across platforms.
These four tools accounted for the vast majority of mentions, suggesting a shift away from the highly splintered LCNC landscape of previous years, where 30+ platforms shared single-digit adoption rates.
The takeaway is clear: while a significant portion of respondents still avoid LCNC workflows entirely, tool usage is diversifying, and AI-assisted or structurally guided platforms like Flatlogic and FlutterFlow are quickly closing the gap with legacy solutions like WordPress.
In 2022 and 2023, LCNC tools were seen as helpful but secondary. In 2024, they entered early production pipelines. By 2025, LCNC tools no longer niche, they are a legitimate and strategic option for a growing segment of the development community, especially in the contexts of MVP validation, prototyping, internal tools, and solo founder workflows.
Learning how to code
In 2025, conversational AI officially became the most preferred way to learn programming, with 30.0% of respondents choosing “AI (talk with AI)” as the most effective method. This marks the first time AI-assisted learning has surpassed traditional educational models and structured online programs.
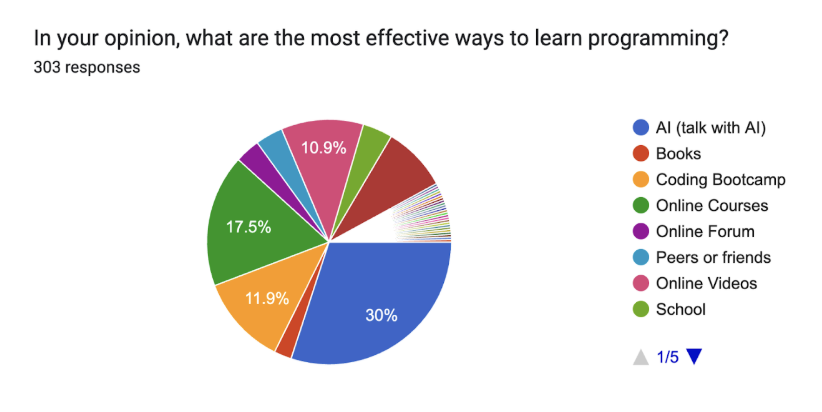
Other popular approaches included:
- Online Courses – 17.5%
- Coding Bootcamps – 11.9%
- Online Videos – 10.9%
- University education – 8.6%
The trend confirms a broader redefinition of what "learning to code" means in practice. Where traditional routes emphasized structured curricula and long-form content, respondents now increasingly rely on interactive, real-time, AI-guided support that adapts to their exact needs.
From 2022 to 2025, learning to code shifted dramatically from traditional methods to AI-driven approaches. In 2022, most respondents relied on online courses and videos. By 2023, AI tools like ChatGPT began gaining traction, used by around 18% of learners. In 2024, AI nearly matched structured learning, reaching 22.6%.
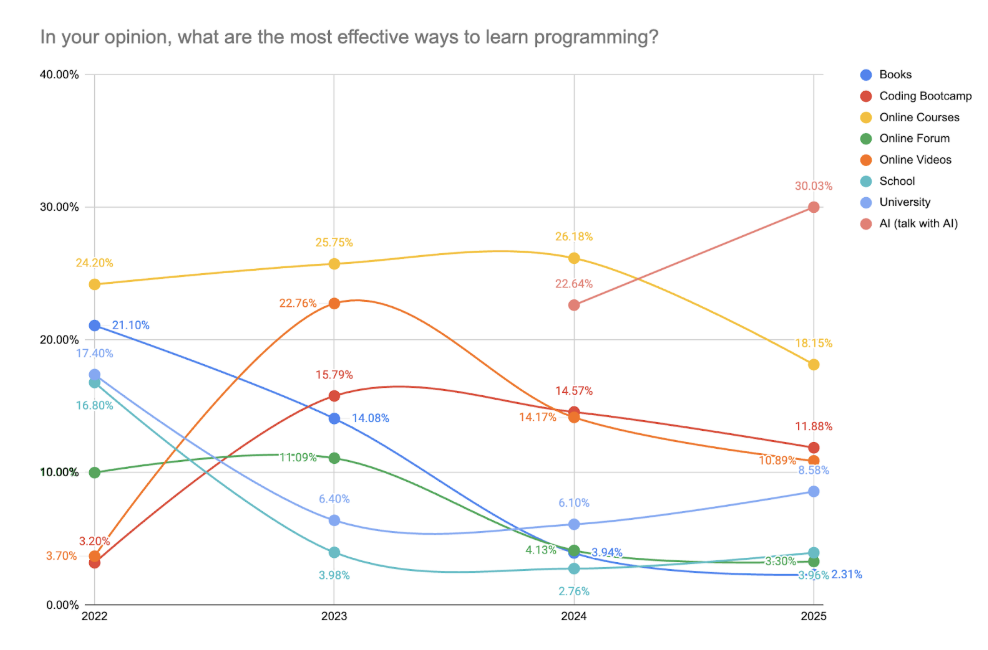
As of 2025, AI is not just assisting the learning process, it is defining it. Respondents now treat tools like ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot as interactive tutors, replacing static tutorials and video content. This shift reflects a broader trend toward on-demand, personalized, and dialog-based learning that matches real-world development challenges.
While universities and bootcamps still play a role, particularly for those seeking structure or certification, the momentum is clearly shifting toward autonomous, AI-supported exploration as the fastest and most accessible way to gain coding fluency.
Technologies and frameworks
To understand technology preferences in 2025, we asked participants to select the frontend, backend, data, and infrastructure tools they use when building web applications. Compared to previous years, the picture is becoming more stable, certain stacks are consolidating dominance, while others are fading into more niche roles.
Web development technologies overall
The dominant trend in 2025 is the continued consolidation around the React + Node.js ecosystem, with AI assistance and backendless stacks increasingly supplementing, rather than replacing, foundational choices. Compared to 2024, where respondents still actively experimented across broader categories, 2025 reveals more confident, opinionated decisions by teams and individuals.
As shown in the chart, AI was the most mentioned technology, followed by Node.js, JavaScript, and React.
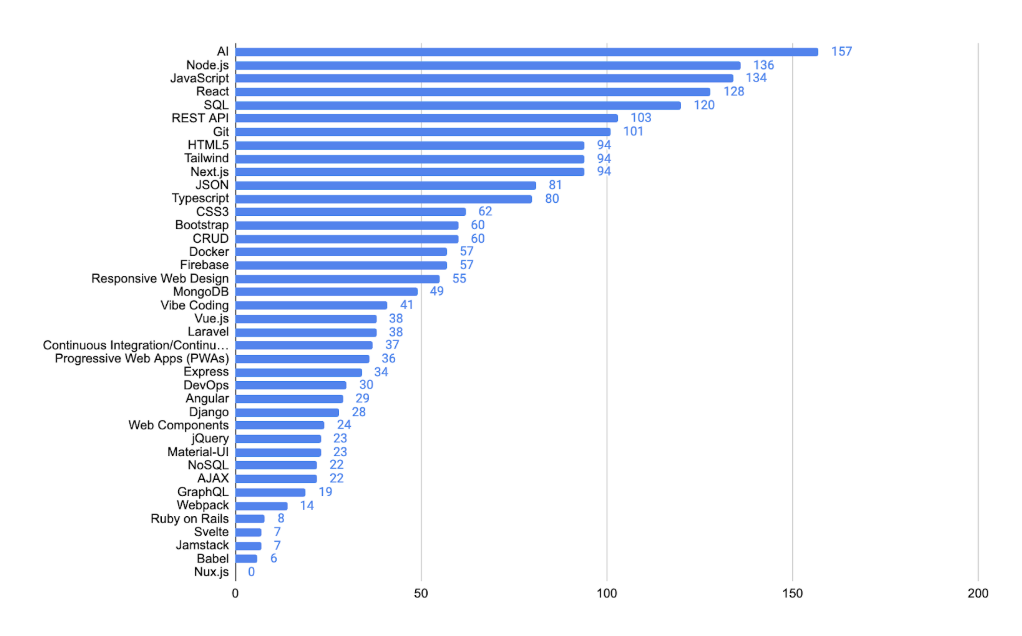
Respondents are moving toward fewer, tightly integrated tools. Traditional choices like jQuery and Ruby on Rails continue to fade, while modern stacks, utility-first CSS (e.g., Tailwind), and backendless solutions like Firebase are gaining ground. The rise of “Vibe-Coding”, AI-enhanced app generation, also reflects growing trust in automation.
In short, respondents are picking tools that offer speed, structure, and compatibility, with AI now fully integrated into that vision.
Front-end technologies
In 2025, React remains the dominant frontend framework, chosen by 43.75% of all respondents. This aligns with its consistent leadership in previous years, 51.8% in 2024 and similar rates in 2023 and 2022. Its popularity is especially high among early- and mid-career respondents, where it often serves as the default choice.
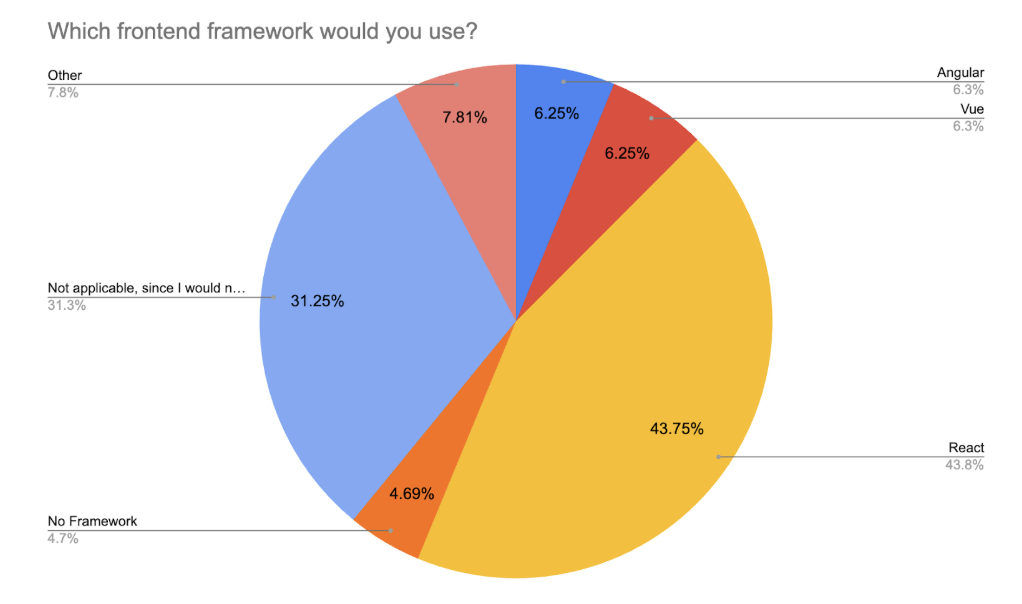
Frameworks like Vue (6.25%) and Angular (6.25%) continue to hold modest adoption, particularly among more experienced respondents or those tied to legacy stacks. However, their usage has remained relatively flat year-over-year.
A notable 4.69% of respondents now report using “no framework”, opting instead for vanilla JavaScript, AI-generated UIs, or lightweight tools like HTMX or Alpine.js. Meanwhile, 31.25% of respondents said they would not write frontend code themselves, highlighting the growing influence of AI-driven platforms, LCNC tools, and backend/frontend abstraction layers.
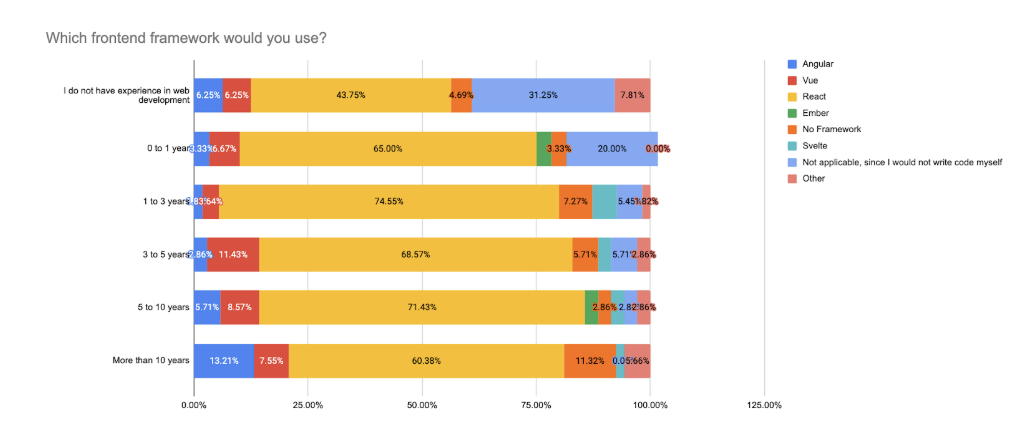
Experience-level data reinforces this trend:
- React usage peaks among respondents with 1–3 years (74.6%) and remains high across all groups up to 10 years.
- Among those with more than 10 years of experience, React still leads at 60.4%, but there’s noticeably more experimentation: 11.3% use no framework, and 13.2% delegate frontend work entirely.
- Beginners (0–1 year) overwhelmingly adopt React (65%), with little deviation toward alternatives.
In summary, React dominates across all experience levels, but senior respondents increasingly explore lighter-weight, composable setups or offload UI concerns entirely via tooling. This suggests React is no longer just a frontend library, it’s the “safe default” for most respondents, while others are beginning to tailor their stacks with more surgical choices.
Back-end technologies
Java has emerged as the most selected back-end technology in 2025, chosen by 33.7% of respondents. This is a notable shift from previous years, where Node.js consistently held the top position. In 2024 and 2023, Node.js was the most popular backend framework, followed by Python and PHP. In 2022, the trend was similar, with Node.js leading, PHP second, and Java third. Now, with 28.4% of respondents choosing JavaScript (Node.js), it remains a strong contender but has been overtaken for the first time in this research series. Python takes the third spot in 2025, preferred by 17.2% of respondents, while PHP (10.6%) remains a stable fourth.
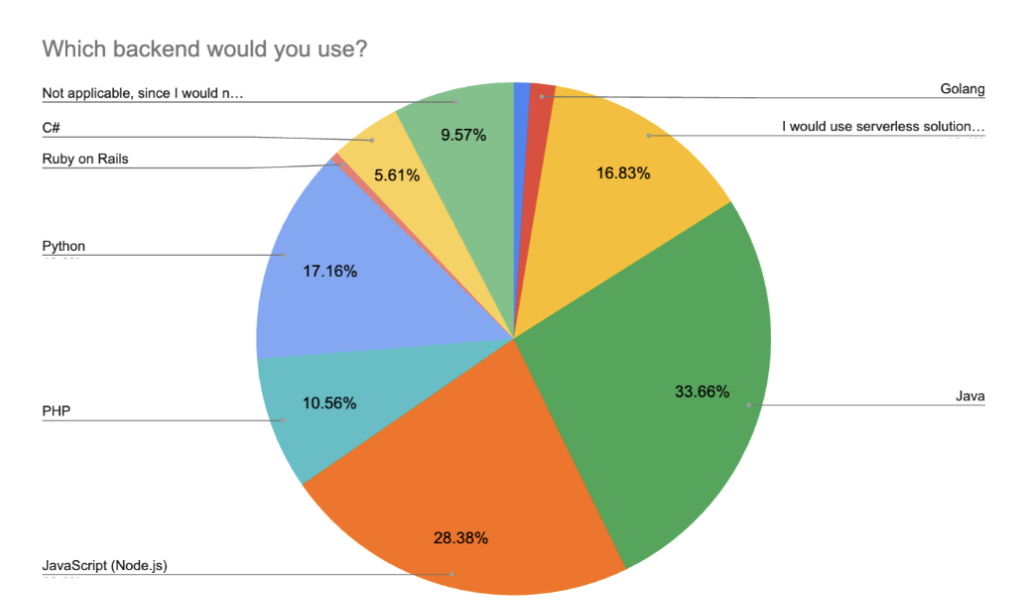
Experience-level trends confirm that respondents with 1–3 years of experience tend to prefer mainstream, accessible technologies like Java, Node.js, and Python. These stacks are valued for their rich documentation, community support, and compatibility with modern frontend frameworks like React.
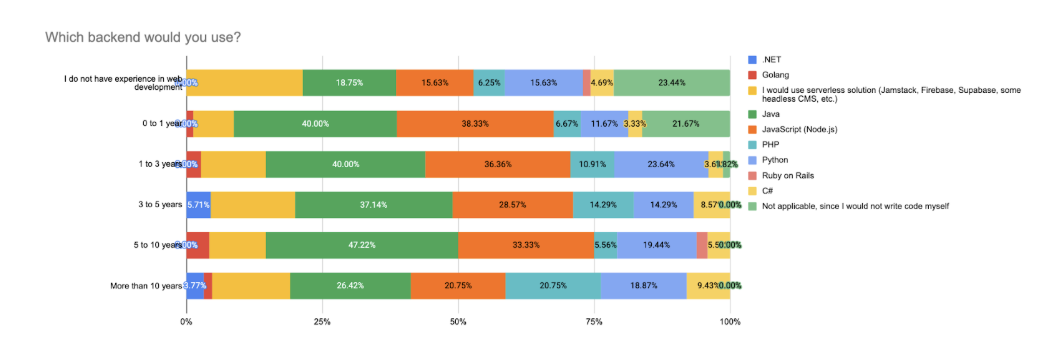
As respondents gain more experience (3–5 and 5–10 years), their choices diversify. Many continue to use the dominant stacks, but a growing number explore serverless solutions or branch into specialized languages such as C# (.NET) and Golang, especially in cases where scalability, performance, or infrastructure needs dictate technology choices.
Among respondents with more than 10 years of experience, Java still leads, but there's increased adoption of Python, C#, and other less common stacks. Interestingly, while some veterans lean into classic enterprise stacks, others report shifting toward backendless models to streamline delivery and maintenance.
Java & JavaScript are clear leaders.
Data management
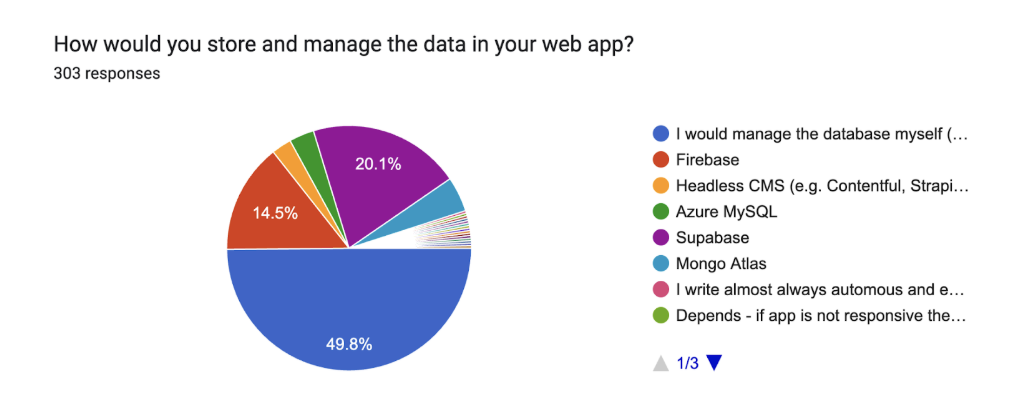
In data storage and management, nearly half of the respondents (49.8%) reported that they prefer to manage their own databases, a slight drop from 2024 and a continuation of the downward trend observed over the past three years. Meanwhile, the use of Firebase (14.5%), headless CMSs, and serverless solutions continues to grow gradually, reflecting the shift toward backendless and AI-assisted workflows.
Among those who do self-manage their databases, PostgreSQL (35%) and MySQL (27%) remain the most popular choices. These two relational databases have consistently topped the list for multiple years, and continue to dominate in 2025. MongoDB (12%) holds its usual third-place position but continues to be less favored by highly experienced respondents. Traditional enterprise tools such as SQL Server (5.6%), MariaDB (3.0%), and Oracle (1.7%) maintain limited adoption, largely within specific organizational or legacy contexts.
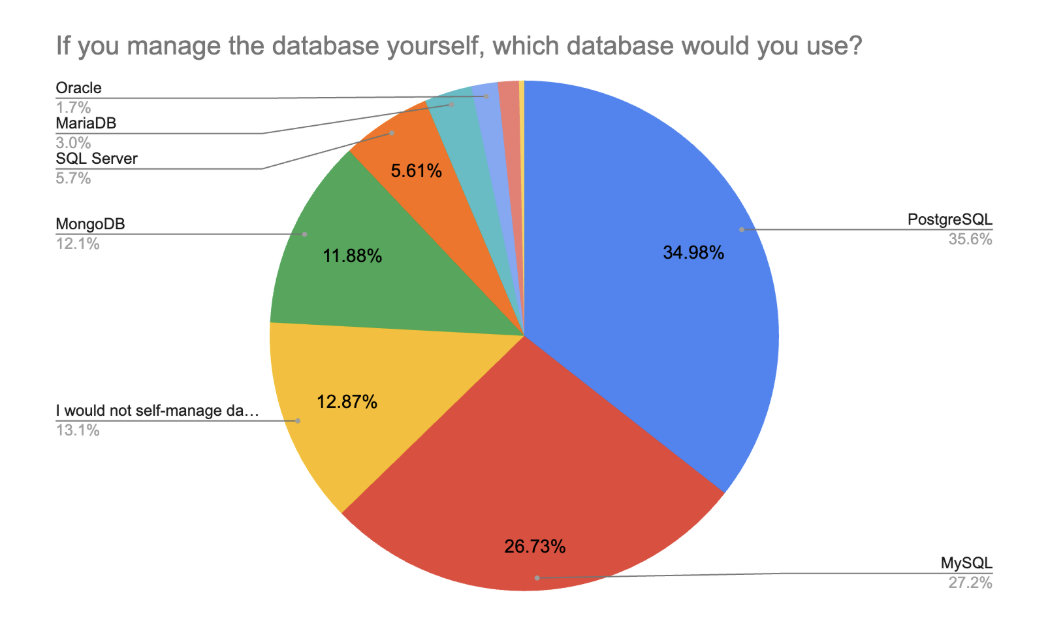
Interestingly, database preference in 2025 shows clearer trends when segmented by experience. While relational databases remain the default across all experience levels, PostgreSQL is now clearly more popular among experienced respondents, especially those with 5–10 years of experience (54.3%) and more than 10 years (49.1%). This marks a reversal of earlier patterns observed in 2022 and 2023, where MySQL was more commonly chosen by senior respondents.
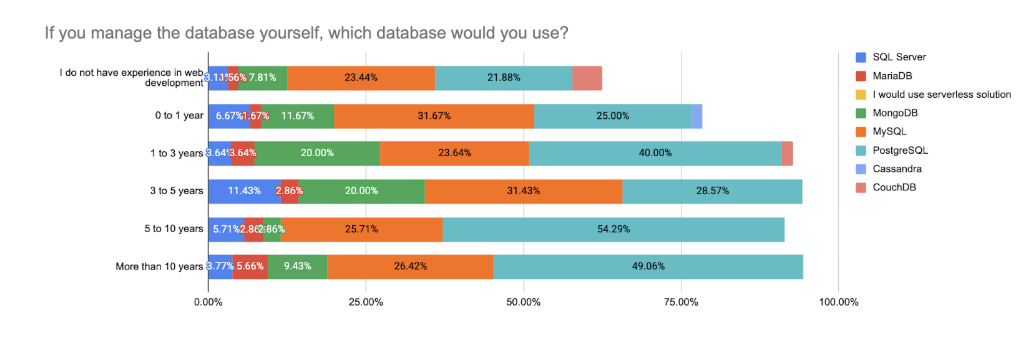
Respondents with less than 3 years of experience show more variety, with higher usage of MySQL, MongoDB, and serverless solutions like Firebase and Supabase. Those just starting (0–1 year) are less likely to manage databases themselves and more inclined to rely on managed infrastructure for simplicity.
Relationship between front-end, back-end, and data management solutions
We also see a strong correlation in the choice of front-end and back-end technologies. Respondents who use React are most likely to choose Java (42.6%) and Node.js (37.8%) as their back-end solutions. This continues the trend observed in 2023, where React was commonly paired with Node.js and Java. In 2022, React users primarily leaned toward Node.js, but in 2025, we see Java slightly overtaking it among React-based respondents, possibly due to increased adoption in enterprise and AI-integrated stacks.
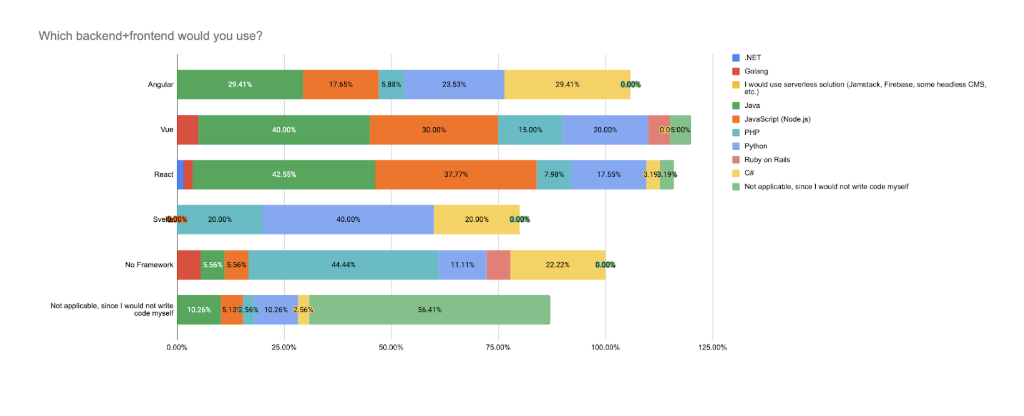
Vue respondents favor Java (40%), Node.js (30%), and PHP (20%), reinforcing Vue’s connection to lightweight, startup-friendly stacks. Angular maintains its alignment with .NET (23.5%), Java (29.4%), and C# (29.4%), reflecting its ongoing enterprise usage.
Some combinations remain predictable: Java + Angular, JavaScript + React, and PHP + Vue are still common stack pairings.
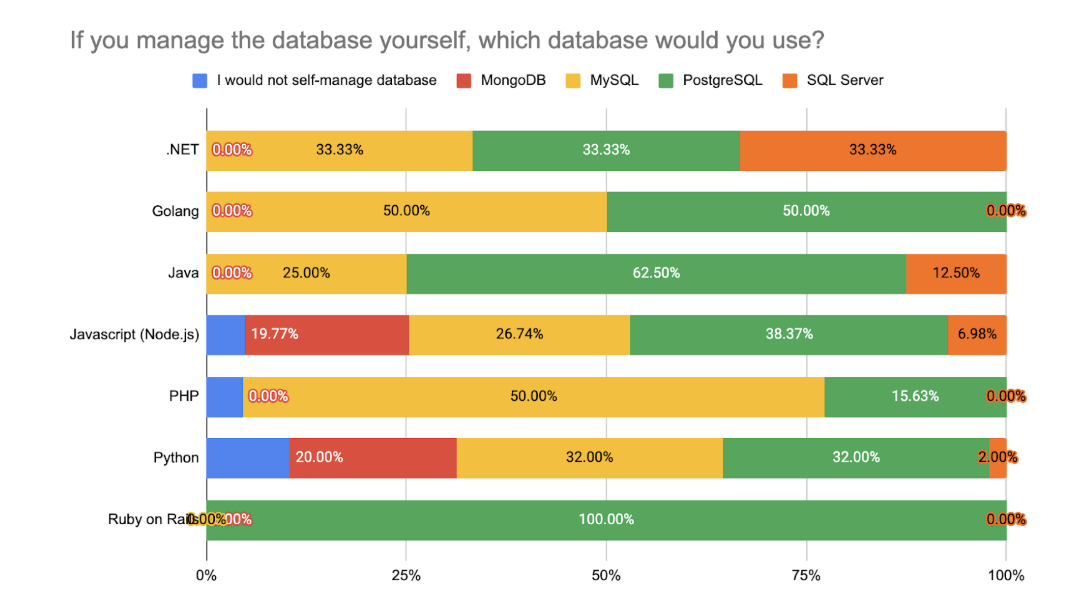
In database preferences, Node.js respondents spread their choices across PostgreSQL (38.4%), MySQL (26.7%), and MongoDB (19.8%), while PHP users overwhelmingly favor MySQL (50%). Java is most commonly paired with PostgreSQL (62.5%), and Python shows balanced usage between PostgreSQL and MySQL.
Traditional stack pairings remain consistent:
- .NET with SQL Server or PostgreSQL
- Golang with PostgreSQL
- Node.js with PostgreSQL and MongoDB
- PHP with MySQL
- Ruby on Rails with PostgreSQL (100%)
Overall, while new tools emerge, most respondents still rely on stable, well-integrated stack combinations built on proven workflows.
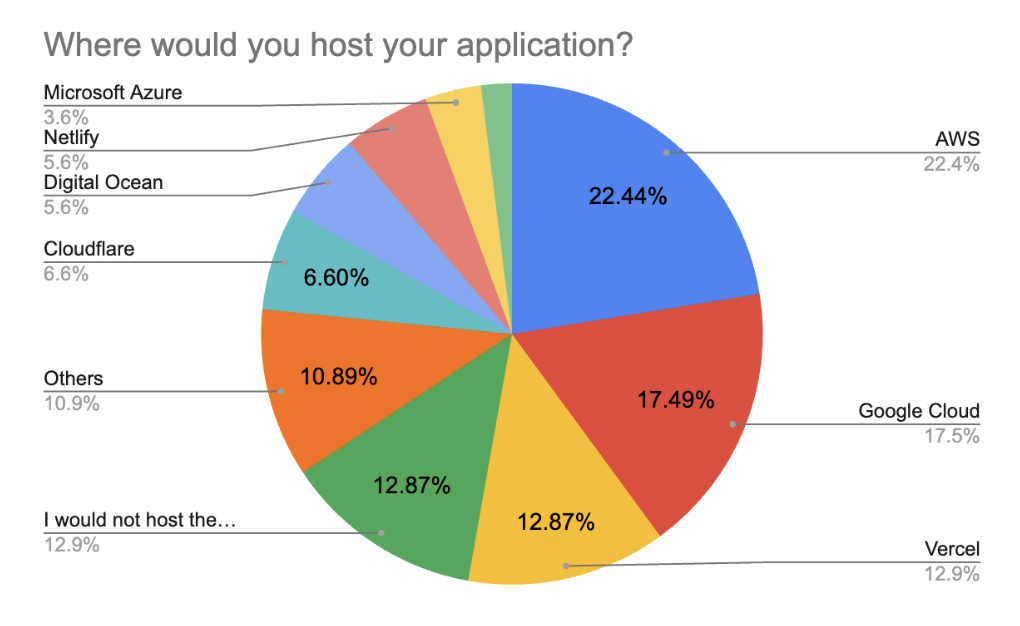
Hosting and Deployment
As far as hosting is concerned, there were no surprises. Amazon AWS is still the leader. This trend is consistent with 2024, 2023, and 2022, where AWS was also the preferred hosting platform.
Code management tools
GitHub is a leader in the go-to option for hosting and managing their code, with a few individuals selecting in-house servers instead. This trend remains consistent with 2024, 2023, and 2022, where GitHub was also the preferred platform for code management.
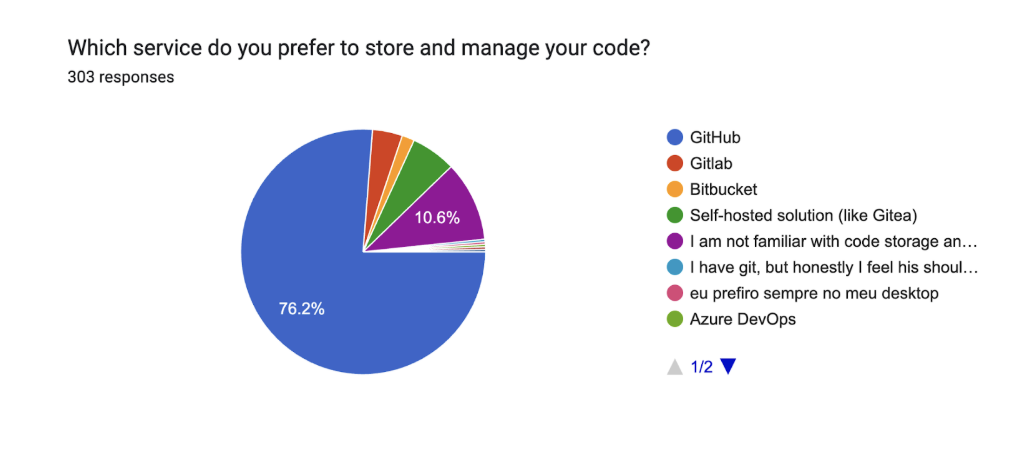
API
More than 67% of engineers prefer REST APIs when setting up web applications. This preference for REST APIs is consistent with the 2024, 2023, and 2022 findings.
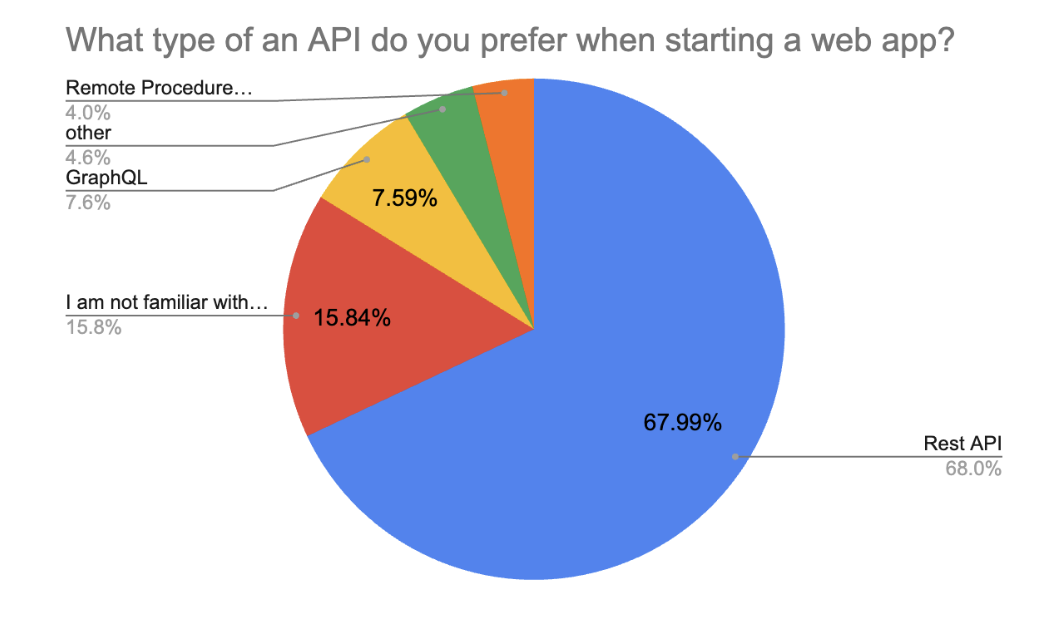
CSS and component libraries
Tailwind CSS has overtaken Bootstrap as the most popular CSS/component library in 2025, with 33.99% of respondents choosing it as their preferred styling tool. Bootstrap now holds second place at 19.47%, followed by Material UI (10.56%). Notably, the “no library, pure HTML” approach has gained more traction, now chosen by 15.51% of respondents, up from 12.4% last year, indicating a growing preference for lightweight, custom-styled UIs or AI-generated layouts. Emerging tools like ShadCN/UI (7.3%) and Ant Design (4.0%) also make an appearance, reflecting the increasingly diverse ecosystem of frontend styling solutions.
Comparison of Web Development Trends and Preferences From 2022 to 2025
Over the four years from 2022 to 2025, the web development landscape has undergone a profound transformation, evolving from manual, code-centric workflows to AI-driven development as the new default. Low-code/no-code (LCNC) tools, once seen as the future, have taken on a more limited, supportive role alongside increasingly powerful AI solutions.
Building Web Applications
The share of respondents preferring traditional, code-only development continues to shrink. In 2022, 65.97% of participants preferred building apps by writing code. By 2023, that number dropped to 56.44%, then to 36.02% in 2024, and now in 2025 it stands at just 20.8%.
At the same time, AI-powered app generation tools, which barely registered in 2022, have rapidly overtaken all other methods. In 2025, 38% of respondents use them as their primary approach. Hybrid workflows, combining coding with LCNC or AI assistance, have grown steadily: from 22.3% in 2022 to 32.7% in 2023, 37.4% in 2024, and 29.7% in 2025, where they have stabilized as a key middle ground for balancing speed and control.
AI is now at the center of the development process. In 2022, AI usage was negligible. In 2023, it appeared in ~18% of workflows. By 2024, 63% of respondents reported using AI tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot. In 2025, that number has grown even further, with 67.2% of those who code choosing to start with an AI-generated codebase, a dramatic shift in just three years.
Technology Trends
From 2022 through 2025, React and Node.js have remained the dominant frontend and backend technologies. React has grown more entrenched across all experience levels, especially among early-career respondents. Java has gained ground in 2025 as a backend favorite, surpassing Node.js in some roles and experience groups.
PostgreSQL and MySQL continue to be the most widely used databases. However, managed and serverless solutions like Firebase and Supabase are gaining traction, particularly among beginners and non-technical users.
AWS has consistently remained the leading cloud hosting provider, although Google Cloud, Vercel, and Cloudflare have expanded their user base. REST APIs are still the most common architecture, but GraphQL is gradually carving out space among React-heavy and frontend-first teams.
Learning and Professional Development
Online courses and video tutorials were dominant in 2022 and 2023. But by 2024, a shift toward AI-assisted learning had become apparent. In 2025, that shift is complete: 30% of respondents now consider AI (e.g., ChatGPT) the most effective way to learn programming, making it the top choice for the first time.
Meanwhile, the popularity of structured online courses has dropped to 18.15%, bootcamps to 11.88%, and video-based learning to just 10.89%. Among beginners (0–1 year), 43.3% consider AI their primary tutor. Across all experience levels, AI is replacing static content with interactive, adaptive learning.
LCNC Tools and AI Integration
In 2022 and 2023, LCNC tools like WordPress and Wix dominated among non-coding users. In 2024, tools like FlutterFlow and Bubble gained attention. In 2025, Flatlogic Platform (25.1%), WordPress (20.8%), and Bubble (13.5%) are among the most cited LCNC tools, but overall, adoption remains fragmented and limited. 28.7% of respondents still say they would not use LCNC tools, down from 32% in 2024 and 45% in 2022.
AI tools, however, are a different story. Once an emerging trend, they’re now foundational. In 2025, AI is used not only to scaffold projects but to define architecture, generate codebases, and guide learning. These tools are embraced by technical and non-technical users alike, though with different expectations. Engineers use AI to accelerate tasks, and non-developers use it to build from scratch.
Engineer Profiles and Preferences
In 2022 and 2023, more experienced engineers favored classical approaches, while less experienced respondents explored LCNC. In 2024, that line began to blur. In 2025, the divide is clearer again, but along different lines. Engineers with 3 to 10 years of experience are most likely to still build by hand, though many also use hybrid approaches.
In contrast, non-technical roles such as founders, PMs, and designers now overwhelmingly rely on AI-based tools to build full applications. Among decision-makers, over 70% use AI-first tools, often skipping traditional LCNC platforms altogether.
Code Management and APIs
GitHub remains the top choice for version control and code hosting from 2022 to 2025. Self-hosted Git and GitLab appear in smaller numbers. REST APIs continue to dominate for service architecture, though GraphQL shows steady growth in frontend-heavy workflows.
CSS and Component Libraries
Tailwind CSS has taken the lead in 2025 with 33.99%, overtaking Bootstrap (19.47%) for the first time. Material UI (10.56%) holds steady. Notably, the "no library" trend continues to rise, with 15.5% now preferring pure HTML or AI-generated UI, up from 12.4% in 2024.
From 2022 to 2025, the web development process has evolved rapidly. Traditional coding has declined, hybrid approaches have matured, and AI has emerged as the dominant force, shaping how applications are built, learned, and deployed. The future of web development isn’t about replacing engineers with AI, but about giving more people, including non-technical ones, the power to build. In 2025, AI isn’t a side tool, it’s the default.
Conclusion
The 2025 edition of our annual research confirms what previous years have gradually revealed: the way web applications are developed is undergoing a fundamental shift. What began in 2022 as an industry dominated by manual coding and exploratory use of low-code platforms has evolved into a new standard defined by AI-assisted development, opinionated full-stack frameworks, and adaptive learning environments.
Over the last four years, traditional coding has declined as the default approach. In 2022, nearly two-thirds of respondents built web apps entirely by hand. In 2025, that number has dropped to just 20.8%. In its place, AI-powered app generators now lead the way, used by 38% of respondents, while hybrid workflows, blending classical coding with AI or LCNC tools, have stabilized at around 30%. Classical drag-and-drop LCNC platforms, once positioned as coding alternatives, have moved into a supporting role, now used by just 6.3% of respondents.
What we’re witnessing is more than a tooling shift – it's the mainstreaming of “vibe-coding”: a workflow where developers interact with AI assistants through chat interfaces or IDE copilots to scaffold, adjust, and evolve applications collaboratively. No longer an experiment, this approach now delivers real outcomes. 31.7% of respondents say they reach Level 3 complexity (frontend + backend), 29.4% go further to full-stack CRUD systems (Level 4), and 14.5% report building production-grade SaaS with advanced features (Level 5). At the same time, concerns persist — including context loss (45.5%), unclear pricing (41.9%), and customization limits (33.3%) — though 11.2% of users reported no issues at all, suggesting growing maturity and trust in these tools.
Technologically, React (62%) remains the dominant frontend framework, while Node.js, Java, and Python lead on the backend. The React + Node.js + PostgreSQL stack remains a reliable default, especially for respondents with 1–10 years of experience. But we also see signs of maturity: more experienced respondents increasingly diversify their tooling, adopting backendless models, infrastructure-as-code, or lightweight alternatives for performance and control.
Database management reflects this same duality. While 49.8% of respondents still manage their databases manually, many now rely on backendless solutions like Firebase and Supabase. PostgreSQL has surpassed MySQL as the most preferred database, especially among experienced engineers, marking a reversal of earlier trends.
AI has clearly moved from the periphery to the center of both development and education. In 2025, 30% of respondents prefer learning to code through AI assistants like ChatGPT, making it the most common learning method, outpacing courses, bootcamps, and university paths. Among beginners, this number jumps to over 43%. AI is no longer just a tool, it’s a tutor, a teammate, and in many cases, the foundation on which entire applications are started.
Tooling choices reflect this new mindset. From GitHub as the near-universal code management platform to Tailwind CSS, now surpassing Bootstrap in popularity, respondents are favoring tools that are lightweight, flexible, and compatible with AI-driven workflows. REST APIs remain dominant, and hosting patterns are unchanged. AWS is still the clear favorite, with Google Cloud and Vercel growing steadily.
Perhaps the most striking shift is cultural. AI is not replacing engineers, it’s democratizing web development. Non-technical users like founders and marketers now launch apps independently, while experienced respondents selectively use AI to accelerate boilerplate tasks and focus on what matters most: business logic, customization, and control. The rise of “vibe-coding,” where developers collaborate with AI through chat interfaces or embedded IDE copilots, signals not just a technical change, but a philosophical one.
To ensure ongoing evaluation of these developments, we plan to continue this research annually. Some patterns, such as the widespread adoption of AI tools and the slow decline of manual coding, are well established. However, other trends remain less clear. The long-term role of LCNC tools, the evolution of text-to-app builders, and the integration of generative AI into full-stack development all deserve deeper exploration. Future editions of this study will help track these changes as they unfold.
The 2025 data paints a clear picture: the future of web development is collaborative, AI-augmented, and increasingly accessible.
For that, please support our research by spreading the word about it, sharing it with your network, and quoting it in your articles! Feel free to leave your comments on our social media pages (X (Twitter), Facebook, Linkedin, and Discord) if you have any suggestions, questions, or criticisms! We are open to discussion and feedback.
If you need raw data - please contact us at [email protected], we will be happy to share.