TL;DR
- React is a UI library; Next.js is a React framework adding SSR/SSG, routing, and optimizations
- Choose Next.js for SSR, API routes, and full‑stack needs; React for SPAs, dynamic routing, offline support
- Next.js offers built‑in TypeScript and file‑system routing; CRA typically needs extra configuration
- Quick start via npx create-next-app or npx create-react-app to scaffold projects
Fact Box
- Next.js was created by Vercel in 2016.
- React was created at Facebook in 2011 and open-sourced in 2013.
- Next.js supports server-side rendering and static generation out of the box.
- Create React App does not support server-side rendering by default.
- Notable Next.js adopters listed: Twitch, TikTok, Hulu, and Binance.
Are you struggling to decide which technology to use for your app? If you’re considering Next.js and React, you might be asking yourself questions such as “What are the advantages of each?”, “How do they compare?”, or “Which one should I choose?” – so don’t waste your time trying to figure out which technology to use.
The dilemma of choosing between Next.js and React has been around for some time, and it is a significant problem for developers who want to create an app with the best possible outcome. Choosing the right technology is essential for a successful product. With the help of the latest research and development, we can now make the right decision more easily.
After reading this article, you will have a better understanding of the differences between Next.js and React. You will also learn which technology is best suited for your application, and the benefits of using it.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is an open-source JavaScript framework for developing fast, lightweight, and easy-to-use web applications and static websites (one-pages) using React. Next.js was created by Vercel in 2016. Next.js requires Node.js and can be initialized using npm. There are a lot of reasons why Next.js has such a strong reputation in the world of application development. They are known for being reliable as they offer image optimization, internationalization, zero-config, Next.js analytics, hybrid: SSR and SGG, fast refresh, API routes, TypeScript support, file-system routing, code-splitting, and bundling, incremental static regeneration, and built-in CSS support, etc.
Next.js includes all the features needed to build an application. Moreover, the documentation is excellent and it is becoming very popular among developers for frontend development. Here are the most popular platforms and apps of Next.js: Twitch.tv, TikTok, Hulu, Binance, and many others that involve a massive number of users engaging with complex data influxes.
What is React?
React is an efficient, declarative and flexible JavaScript library for building interactive UI, inspired by xHP, the HTML component library for PHP. React was created by Facebook in 2011 and then open-sourced in 2013.React is used to create dynamic, mobile apps, one-pages, visualization tools, and dashboards. Here are some of the most popular platforms and apps created with React: Facebook, Netflix, Atlassian, Airbnb, Dropbox, Reddit, etc. 
Next.js vs React
Even in a sea of JavaScript frameworks and libraries, React and NextJS stand out. React is the most popular JavaScript library for frontend developers. NextJS, although smaller than React, has grown continuously over the years and is well on its way to becoming the most-used JavaScript framework. So, let’s compare React and Next.js. React – is a JavaScript library for building UI. Next.js – is the React framework. NextJS is used on top of React, extending its features and optimizing the development process: React doesn’t even have to work with NextJS, but NextJS uses React to deploy applications.
React has a special framework – Create React App, an application used to create React projects and includes tools such as Babel, Webpack, and ESlint. Next.js is a React-based framework that allows you to build applications with server-side rendering. React is still the core of the application, but the structure and navigation mechanisms (architecture) – are defined by Next.js. The difference between a framework and a library is that a framework has more features and focuses on several aspects of development, and gives you rules and guidelines for writing code and structuring files.
| Next.js | React & Create React App (CPA) | |
|---|---|---|
| Server-Side Rendering (SSR) | Supports different types of SSR. – Static generation: obtaining data at build time. Best suited for use cases such as blogs or static websites. – Server-side rendering: sampling data and rendering for each request. May be needed when you need to serve different views to different users. | Doesn’t support SSR out of the box. However, you can still set it up. It just takes more effort to configure SSR with your preferred server and configuration. |
| Configuration | Almost everything is configurable. If you check the example NextJs templates, you can see files like babelrc, jest.config, eslintrc etc. that you can configure. | Doesn’t leave you much space to configure it. Configurations, such as webpack config, cannot be changed unless you do not deviate from the usual CRA path (eject, rescripts, rewired, craco). You should use what is configured in react-scripts, which is the core of CRA. |
| Maintainability | Well maintained. Release regular updates. | Very sensitive. If you keep up with updates of CRA releases, it is not difficult to maintain. |
| TypeScript | Supports typescript out of the box. Configurations for TypeScript: touch tsconfig.json | Supports. You can initialize the CRA app with typescript like this:npx create-react-app my-app --template typescript |
| Hooks Support | Supports | Supports |
| Redux Support | Supports | Supports |
| Performance | Incredibly fast apps thanks to static sites and server-side rendering. | Decent, but the lack of code splitting results in poor performance. |
| Community | Tiny, but friendly | Both huge and friendly |
| Features | Support static exports, and pre-rendering, and has a lot of features, for example, automatic building size optimization, fast development compilation and preview mode. | Easily extensible, can include routing as well as management patterns with libraries. |
| Talent pool | Narrow | Broad |
| Easy to learn | Easy | Easy |
| Development costs | Low | Low |
Which one is better?
It’s hard to say that one is better than the other. Remember, React.js is a JS library – a set of tools you can use to build UI – and Next.js is a framework – the blueprints and rules you need to build an entire app – based on React so it’s not a pick this one instead of the other situation.
Use React when:
- You need a highly dynamic routing
- You’re already familiar with JSX
- You need offline support
Use Next.js when:
- You need an all-inclusive framework
- You require backend API endpoints
- You need server-side rendering
What do React vs Next.js projects look like
React
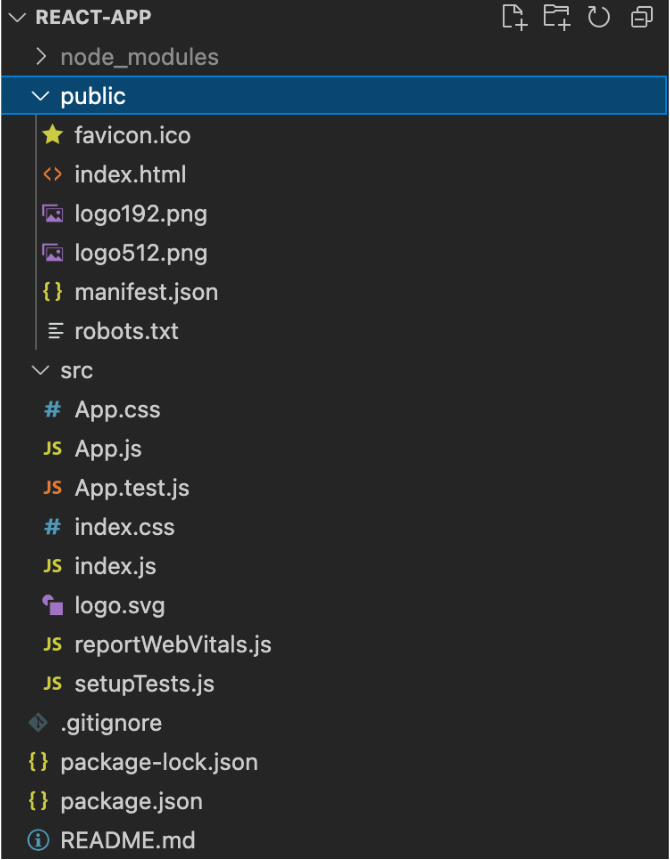
You can get started with React by installing Node.js on your machine and running npx create-react-app react-app. This will create a basic project structure with the src/App.js file as the entry point for the application. You’ll also have a public folder where you can store assets, and the initial scaffold looks like this:
Next.js
With Next.js, you can get started by running npx create-next-app next-app. This will scaffold out a project that already has a pages folder for the pages or routes and a public directory that hosts your assets. The initial scaffold looks like this:
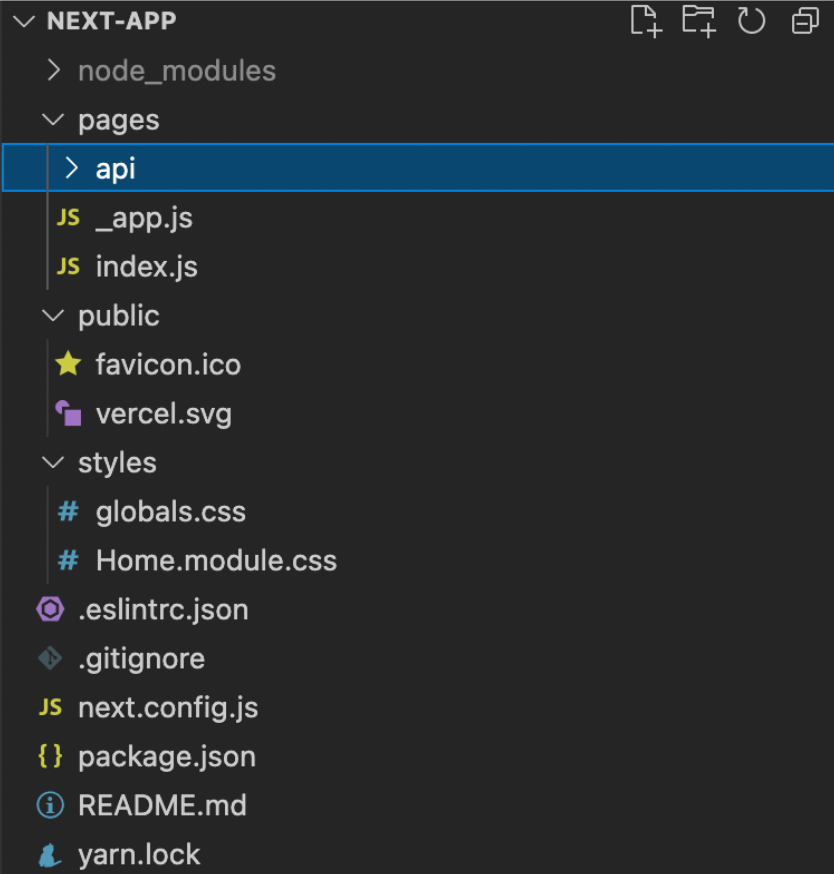
The files in the pages directory relate to routes in your application. The public directory stores your static files or images that you want to serve and can be directly accessed – no need to use require or other React traditional methods to import images into components.
Building Next.js and React projects with Flatlogic
The Flatlogic platform is a great way to bridge the gap between developing your applications. Applications usually use the same elements and components, when using the same technologies. The main thing that distinguishes them on a technical level is the database schema, which implements different data processing and storage mechanisms. The Flatlogic Platform allows you to create applications by combining parts and creating only those that need to be unique. Here you can see how to use the Flatlogic Platform to create Next.js, React applications, and other options for creating CRUD applications on the React. To generate your Next.js or React application, tap here and let’s go.
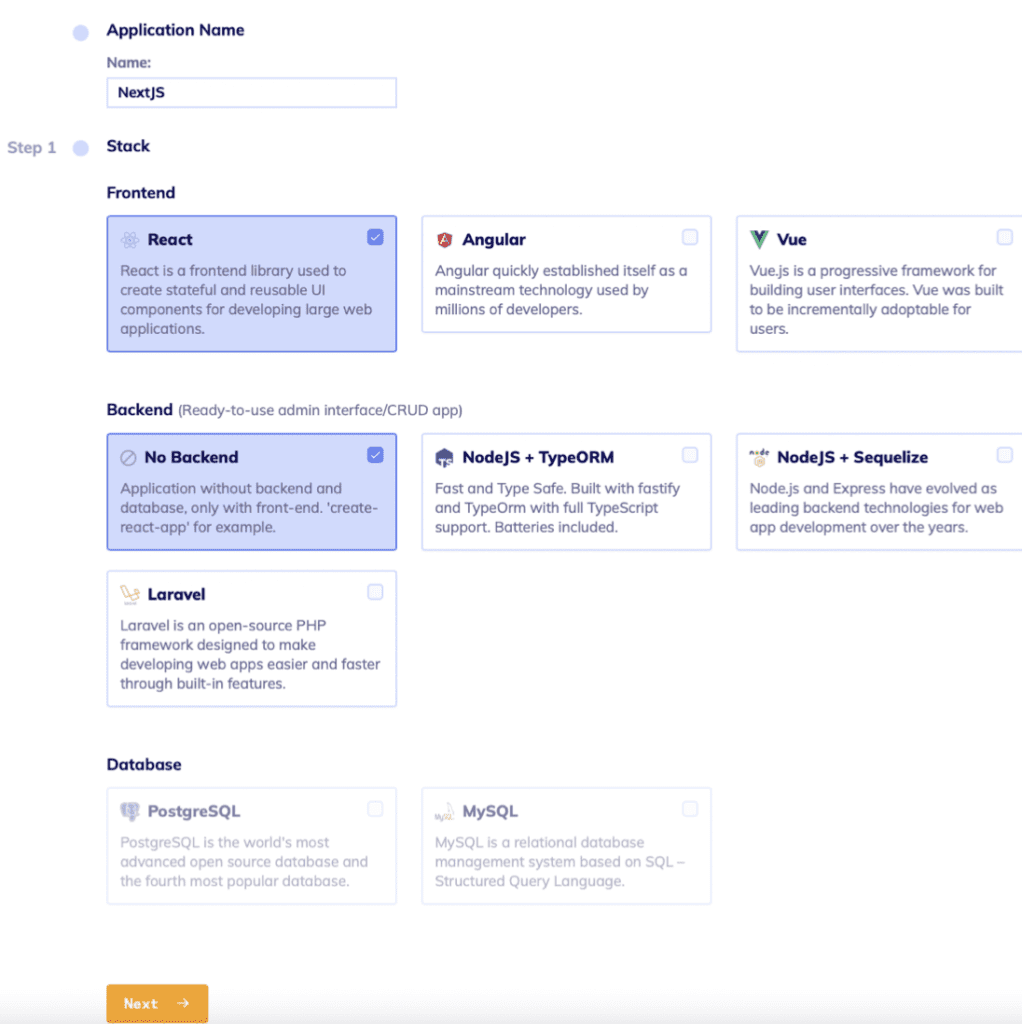
Step 1
Name your project and choose the tech stack: React as frontend and No-backend as backend.
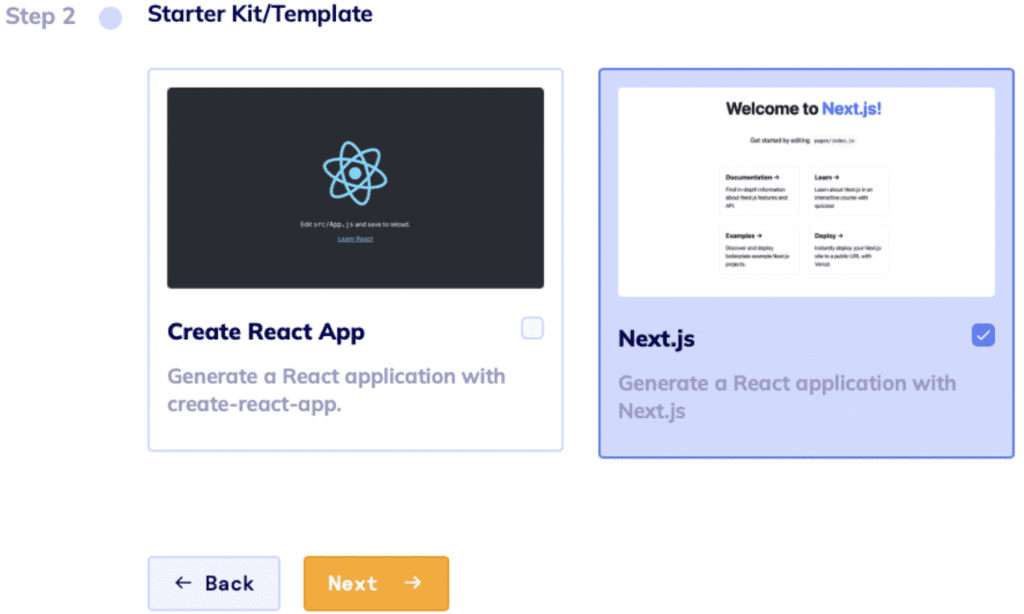
Step 2
Choose the Starter Kit. Here you need to decide which starter kit is best for your project: Next.js or Create React App.
Next, you need to connect your GitHub repository and check the stack and starter kit and Finish the creation process.
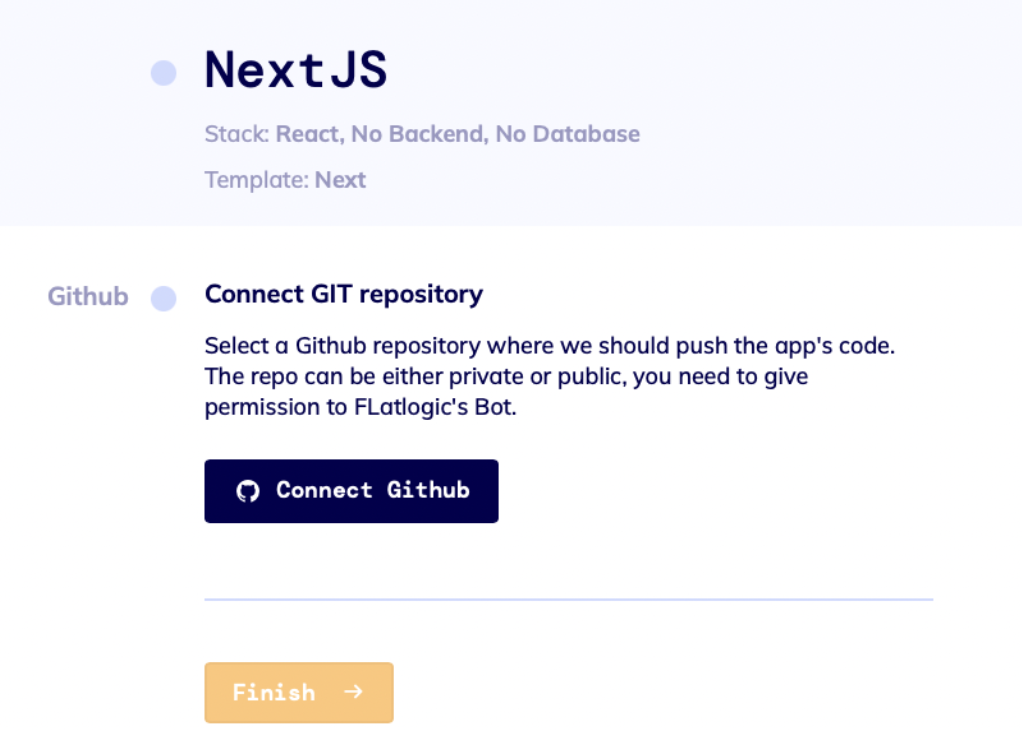
Then you will be redirected to the project settings where you will need to deploy your application.
Conclusion
React and Next.js are new and useful tools for your project, but only for certain tasks. When you choose Next.js, it offers the best solutions for server-side rendering and static website development. It also makes it easy to manage projects with a variety of tools and features.
On the other hand, React is the best choice for developing UIs for one-page applications. Being mobile and web-enabled, it works with a layer of mobile and web applications to create more appealing and intuitive ones. In a nutshell, Next.js offers various tools and features to minimize the development process while React has better resources for the frontend development of your mobile and web applications.
Comments