TL;DR
- AI vibe-coding speeds delivery from static sites to enterprise SaaS via a five-level complexity ladder
- Leading tools handle L1-L4; L5 is reachable with schema-first specs, deterministic code, tests, and human oversight
- Flatlogic study: AI generation leads new starts (38%); manual coding trails (20.8%); 84% use AI in workflows
- Guardrails: formal specs, CI/testing, RBAC/security, version control to curb context, pricing, and integration risks
Fact Box
- 84% of respondents integrate AI tools into their workflows Source
- Nearly 38% use AI-driven generation to start new projects Source
- Fully manual coding is preferred by 20.8% of respondents Source
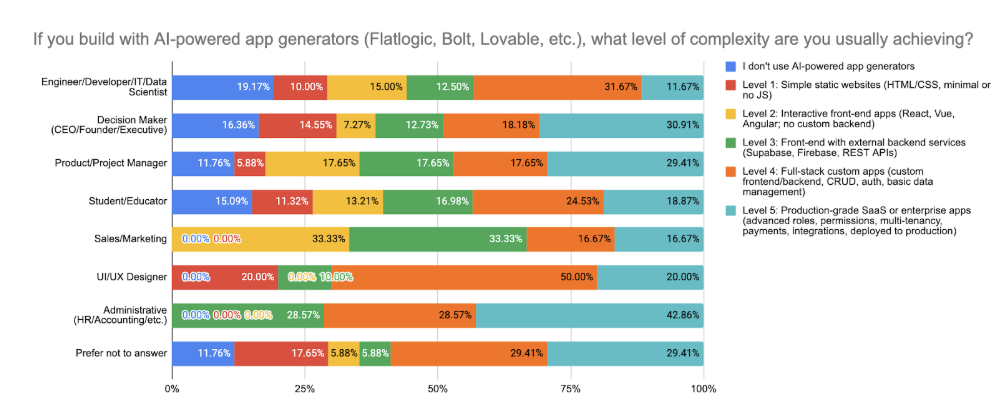
- 31.7% of AI-driven projects reach Level 3 (frontend + backend integration) Source
- 14.5% of AI-driven projects reach Level 5 (production-grade SaaS) Source
Imagine building a fully functional, complex web application without manually writing thousands of lines of code. Today, “vibe-coding” tools claim to make this possible-but how far can they truly go?
When considering vibe-coding tools, you might wonder:
- Can AI-based app generators produce reliable, production-grade software?
- At what level of complexity do these tools become ineffective?
- What risks arise when relying on vibe-coding tools for serious business apps?
- How do you effectively blend rapid AI coding with robust software engineering practices?
The explosive rise of AI-driven coding tools, or “vibe-coding,” has dramatically changed software development practices. According to Flatlogic’s 2025 research, over 84% of respondents are integrating AI tools into their workflows. However, building genuinely complex apps still presents significant challenges, including maintaining code quality, security concerns, and effective project governance.
This article is trustworthy because it draws upon Flatlogic’s comprehensive “Starting Web App in 2025” industry study. Flatlogic specializes in AI-driven enterprise-grade software generation, deploying dozens of production-level applications through structured AI-assisted development.
By reading this article, you will:
- Understand essential terminology around AI-based app development tools
- Explore a five-tier complexity ladder based on concrete research data
- Learn a structured method to create complex web apps using Vibe-coding tools reliably
- Identify common pitfalls and guardrails essential for developing enterprise-grade applications
How Complex Apps Are Built with Vibe‑Coding Tools
Vibe-coding tools have revolutionized how users build complex software, significantly accelerating the process of transforming ideas into functioning applications. At their core, vibe-coding tools allow developers and non-developers alike to describe applications using natural language prompts. AI engines translate these prompts into functional, deployable codebases or software components. The technology powering these tools typically includes advanced language models, deterministic code generators, integrated development environments (IDEs), and collaborative interfaces. 
While early vibe-coding tools primarily tackled simple prototypes and static websites, the landscape has rapidly evolved. Modern tools can now reliably create sophisticated applications ranging from front-end integrations with backend services to fully customized, enterprise-grade software solutions. This spectrum is best visualized as a complexity ladder:
- Level 1 (L1): Static or informational websites without interactivity.
- Level 2 (L2): Interactive front-end applications without custom back-end logic.
- Level 3 (L3): Front-end applications integrated with backend-as-a-service (BaaS) solutions, such as Firebase, Supabase, or REST APIs.
- Level 4 (L4): Custom full-stack applications, featuring databases, authentication, CRUD operations, role management, and data migrations.
- Level 5 (L5): Fully-featured, enterprise-grade SaaS applications including multi-tenancy, advanced role-based access control (RBAC), payment integrations, auditing, scalability, and robust monitoring.
Today’s leading vibe-coding platforms comfortably handle Levels 1 through 4, with certain advanced platforms capable of achieving Level 5, provided specific engineering disciplines are rigorously applied. Successful use-cases at the higher complexity levels typically involve:
- Schema-first approach: Clearly defined data structures, relationships, permissions, and business logic established upfront, enabling deterministic code generation.
- Human-in-the-loop: Developers maintain active oversight, ensuring generated code aligns closely with business requirements, security best practices, and performance standards.
- Deterministic code generation: Utilizing structured frameworks and opinionated technology stacks (React/Next.js, Node.js, PostgreSQL, Tailwind CSS) to ensure consistency, maintainability, and scalability.
- Robust governance & testing: Strong continuous integration (CI) pipelines, comprehensive unit and integration tests, security audits, and controlled deployments.
Common Market Pitfalls and Mitigations:
Despite their strengths, vibe-coding tools come with challenges that must be proactively addressed for successful outcomes:
- Architectural ambiguity:
Developers relying solely on natural language prompts risk inconsistent application structures.
Mitigation: Always employ formal schemas and architectural decision records (ADRs) to clearly document application structure and design choices. - Security gaps:
Generated applications may omit critical security features such as detailed role management, secure handling of sensitive data, or proper authentication.
Mitigation: Integrate security practices early, including role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and automated security testing. - Integration complexity:
Applications frequently require complex third-party integrations that can easily fail or become fragile.
Mitigation: Employ rigorous integration testing, clearly define API contracts, and implement robust error handling and retry mechanisms. - Scalability constraints:
Automatically generated code might not always consider future growth or heavy user traffic.
Mitigation: Incorporate scalability tests and design patterns early, regularly benchmarking performance and optimizing infrastructure. - Context loss and specification drift:
AI assistants might lose context over extended interactions or large-scale projects, causing inconsistencies or redundant work.
Mitigation: Document decisions explicitly, maintain concise task scopes, and regularly reaffirm context through structured prompts.
In conclusion, vibe-coding has matured beyond early experimental use-cases, empowering teams to rapidly build complex, robust, and scalable applications-provided they balance AI-driven acceleration with disciplined software engineering practices.
How Complex Apps Are Built: Insights from Flatlogic’s Industry Study
The landscape of web app development has dramatically shifted, with AI-driven generation tools now dominating as the preferred method for launching new projects-used by nearly 38% of respondents. Traditional, fully manual coding has notably fallen behind, favored by only 20.8%, while hybrid approaches combining AI and manual techniques capture approximately 29.7% of the market. This data clearly highlights the industry’s accelerating move toward automation and AI-driven efficiency, especially in the early stages of development.
Moreover, teams adopting these AI tools aren’t limited to basic applications. Our findings show substantial progress in app complexity: about 31.7% of AI-driven projects successfully combine frontend and backend integrations (Level 3), 29.4% create complete full-stack CRUD apps from scratch (Level 4), and an impressive 14.5% have reached sophisticated, production-grade SaaS applications with advanced features like multi-tenancy, intricate role management, and integrated payment systems (Level 5). AI-powered tools are rapidly redefining what’s achievable in modern software development.
Despite the advantages, respondents highlighted several recurring challenges:
- Context Loss: Maintaining context consistently across project stages remains difficult, especially in lengthy or complex workflows. Poor context management leads to errors, duplicated effort, and reduced productivity, necessitating rigorous documentation practices and well-defined task scopes.
- Pricing Uncertainty: Developers frequently find it difficult to predict accurate costs when using AI-driven tools. Ambiguous or unclear pricing models often cause budgeting issues, highlighting the critical need for transparency and predictable pricing structures.
- Security Concerns: Security becomes a critical challenge as app complexity grows. Developers must integrate comprehensive security planning early to avoid vulnerabilities, data breaches, and compliance issues that emerge in more complex environments.
- Customization Limitations: AI-generated code may lack flexibility or depth needed for specialized or highly unique scenarios. Balancing AI-driven automation with manual customization and advanced feature development is essential to prevent limitations down the road.
- Integration Complexity: Smooth integration of diverse external APIs, services, and third-party software can prove challenging. Teams must pay special attention to integration management, implementing strong testing and monitoring frameworks to prevent disruptions or conflicts.
Understanding the Complexity Ladder
Flatlogic uses a structured model called the “Complexity Ladder” to clearly define benchmarks for application complexity:
- Level 1: Simple static websites with limited functionality.
- Level 2: Interactive front-end applications without custom backend logic.
- Level 3: Front-end apps connected to backend services, such as Firebase or REST APIs.
- Level 4: Full-stack CRUD applications with custom databases, authentication, and business logic.
- Level 5: Comprehensive enterprise SaaS apps featuring multi-tenancy, complex permission management, payment integration, and robust deployment environments.
Best Practices for Building Complex Apps with Vibe-Coding Tools
To achieve success at higher complexity levels, Flatlogic recommends a structured methodology:
- Formalize Application Specs: Clearly define all app components, including data models, relationships, user roles, and interfaces, using structured schemas rather than relying on informal prompts alone.
- Deterministic Code Generation: Convert structured specifications into predictable, maintainable codebases. Deterministic generation minimizes variability and ensures consistency.
- Early Guardrails: Implement comprehensive testing, robust security checks, strict type safety, and deployment standards from the project’s onset.
- Controlled AI Iterations: Enable AI-driven code improvements within clearly defined boundaries, guided by human oversight through pull requests, thorough testing, and code reviews.
- Rigorous Version Control: Maintain strict version control practices, such as using Git workflows, to facilitate rollback and stabilize development environments.
Common Pitfalls & Crucial Safeguards
Flatlogic’s research also identifies frequent pitfalls in using vibe-coding tools and offers actionable strategies to mitigate them:
Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Using informal prompts for critical architectural decisions.
- Blindly trusting AI-generated code without meticulous human review.
- Introducing unnecessary complexity prematurely (like premature microservice architectures).
- Delaying essential security considerations until late in the project lifecycle.
Recommended Guardrails:
- Document all architectural decisions explicitly in schemas or structured decision records.
- Use automated testing frameworks and manual code reviews for every AI-generated contribution.
- Adopt thorough security, compliance, and governance practices from day one.
- Set clear boundaries and establish firm control over AI-driven code and resource utilization.
In summary, Flatlogic’s insights underscore that AI-based development has dramatically reshaped software engineering, allowing teams to create sophisticated, scalable, and secure applications-provided that they follow disciplined development methodologies and implement structured safeguards.
Top 8 Vibe-Coding Tools Based on Flatlogic Research
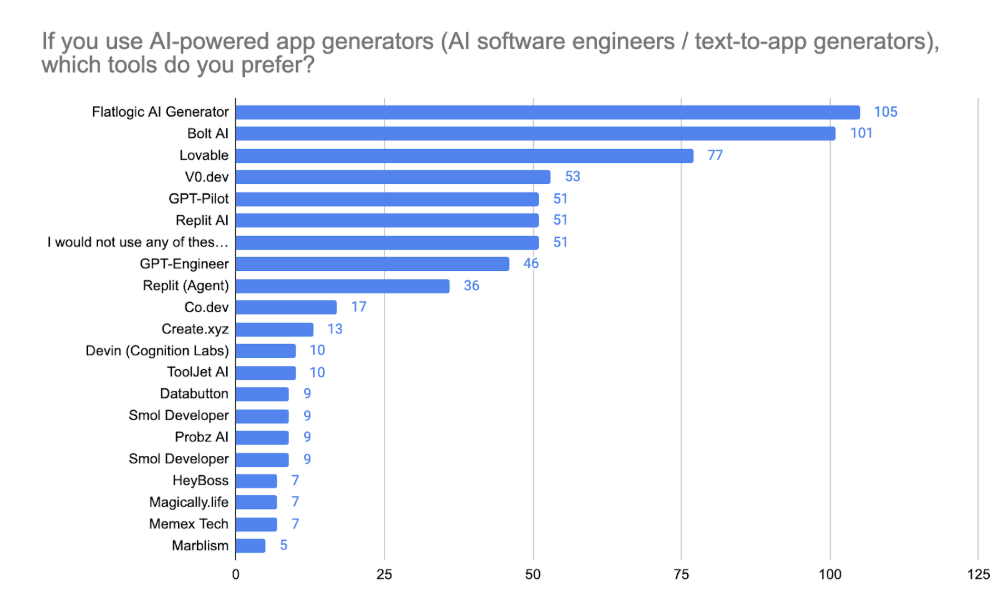
Flatlogic AI Generator
Flatlogic AI Generator is an AI-powered platform that converts plain English descriptions into structured, production-ready web applications. It emphasizes deterministic, schema-based code generation to ensure reliability and scalability. Ideal for complex business applications, it automates deployment and includes robust version control. It suits developers seeking predictable results with enterprise-grade quality.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 4-5 (Full-stack CRUD, Enterprise SaaS)
- Pricing: Free tier available; premium subscriptions tailored for enterprises
- Key Features: Schema-first modeling, deterministic code generation, built-in Git integration, automated deployment
- Pitfalls: Requires upfront structured specs, potentially limiting spontaneity
Bolt AI
Bolt AI facilitates rapid software creation through AI-driven component and feature generation from natural language prompts. Designed primarily for startups and agile teams, it excels at quickly turning ideas into functional prototypes. It supports collaborative, iterative workflows and rapid modifications. However, it may lack the deeper customization flexibility required for more specialized applications.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 2-4 (Moderate complexity, prototyping, MVPs)
- Pricing: Subscription-based; tiered plans based on team size and usage
- Key Features: Rapid prototyping, real-time collaborative development, intuitive UX/UI generation
- Pitfalls: Limited advanced customization and control over architecture details
Lovable
Lovable is an intuitive AI-powered app builder, enabling rapid creation of visually attractive web and mobile applications. It prioritizes simplicity and user experience, suitable for consumer-facing products, marketing sites, or straightforward business apps. Developers can visually build and customize interfaces without coding. Its primary drawback is potential scalability and backend customization limitations.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 2-4 (Consumer apps, moderate complexity projects)
- Pricing: Free tier and scalable paid plans based on feature sets and resource usage
- Key Features: Drag-and-drop interface, visual UI builder, automatic responsive design
- Pitfalls: Limited backend flexibility, less suitable for highly customized enterprise apps
V0.dev
V0.dev leverages AI to convert user interface designs directly into functional front-end code efficiently. Targeted mainly at designers and front-end developers, it significantly reduces UI development time. It suits static sites and moderately interactive applications requiring rapid turnaround. However, complex backend integration and custom business logic require manual intervention and additional tooling.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 1-3 (Static to moderately interactive apps)
- Pricing: Free base tier, premium subscriptions for additional features, and team collaboration
- Key Features: Design-to-code automation, intuitive user experience, code preview, and export
- Pitfalls: Limited support for backend complexity and detailed logic implementations
GPT-Pilot
GPT-Pilot assists developers by transforming natural language descriptions into executable and refined code snippets interactively. It helps streamline code-writing and debugging processes significantly. Ideal for iterative and agile development, it provides multi-language support. Developers need careful oversight due to potential inaccuracies or hallucinations in the generated code.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 2-4 (Moderately complex apps, iterative enhancements)
- Pricing: Usage-based pricing, typically dependent on API calls or token consumption
- Key Features: Interactive coding assistant, real-time debugging help, multi-language support
- Pitfalls: Requires rigorous review due to potential inaccuracies or misunderstood instructions
Replit AI
Replit AI enhances the collaborative browser-based coding environment with AI-powered code suggestions and debugging support. Popular for educational use and prototyping, it offers instant deployment options and simplifies code management. It caters mainly to simpler projects or moderate complexity applications. Its limitations include scalability, security controls, and sophisticated integration challenges.
- Level of Complexity: Levels 1-3 (Educational, prototype projects, simple apps)
- Pricing: Freemium model with optional paid tiers for advanced features
- Key Features: Browser-based IDE, collaborative coding, instant deployments, automated suggestions
- Pitfalls: Limited suitability for highly scalable or security-sensitive enterprise applications
Conclusion
The rapid evolution of vibe-coding tools has fundamentally reshaped the landscape of web application development, enabling teams to efficiently create sophisticated software with significantly reduced manual coding effort. As Flatlogic’s comprehensive research demonstrates, AI-powered generators have become the leading choice for starting new applications, driven by their ability to rapidly and reliably produce increasingly complex solutions.
However, harnessing vibe-coding successfully requires awareness and proactive management of its inherent challenges. Common issues such as context loss, pricing uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and integration complexities highlight the necessity for structured workflows and disciplined engineering practices. To truly unlock the potential of vibe-coding, developers must combine AI-driven rapid development with established methodologies such as schema-first specifications, deterministic code generation, rigorous testing, and robust project governance.
Ultimately, vibe-coding tools empower teams to transcend earlier limitations, making Levels 4 and even 5 on the complexity ladder achievable in real-world scenarios. But the technology alone is not enough-teams must actively mitigate pitfalls by integrating best practices, maintaining human oversight, and clearly defining boundaries for AI-driven tasks. By adopting this balanced approach, organizations can confidently leverage vibe-coding tools to build reliable, secure, and scalable applications in a fraction of the time traditionally required.